- LAW OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND
- FACTORS OF PRODUCTION
- CONCEPT OF NATIONAL INCOME
UNIT 2 – NATIONAL INCOME– PART 1
NATIONAL INCOME
The Economic Wealth, or wellbeing of a country does not depend merely on the possession of resources but also hoe these are used in generating a flow of production and distribution and the consequent income and wealth generated in that process. Hence people combine energies with natural and man-made environment within certain social and technological structure to generate a flow of production. In modern economies this flow of production are translated into goods and services produced by individuals and enterprises in that economy.
Therefore the measurement and accounting of this wealth generated in terms of aggregate Goods And Services produced in an economy is National Income and its accounting process. This this chapter we will look at the basic concepts and terms in national income and the methods of its assessment.
Let’s Learn Some Basic Terminologies.,
MARKET
A market is a place where buying and selling of goods and service takes place. Markets are dependent on two major participants, (i.e.) Buyers & Sellers
- MARKET WITH PHYSICAL SPACE:
Here Buyers and sellers meet together in order to carry on transaction of goods and services.
- MARKET WITHOUT PHYSICAL SPACE: (eg) stock market
Here Buyers and sellers don’t come in direct contact with each other.
LAW OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND
The number of buyers and sellers involved will have a direct bearing on the price of the good or service to be sold, and it is said to be called law of supply and demand.
SUPPLY AND DEMAND RELATIONSHIP
If there are More Seller than buyers for a particular commodity, price of the commodity will decrease due to low demand.
If there are More Buyers than sellers for a particular commodity, price of the commodity will increase due to high demand.
DEMAND
“…Demand refers to the quantity of a goods or a service, which is desired by the buyers at a particular price, all other things unchanged…”
For e.g. 100 buckets of Tomatoes are sold each month in a particular city at a price of Rs.50 per bucket, that quantity of 100 buckets of tomatoes demanded per month at a rate of Rs.50. If the price were Rs.60, we would expect the quantity
demanded to be less. If the price were Rs.40, we would expect the quantity demanded to be more.
SUPPLY
Supply is a fundamental economic concept that describes the total amount of a specific good or service that is available to consumers. It also refers to the amount of a certain goods that producers are willing to supply when receiving a certain price. It depends on production of goods.
COST
Cost is defined as the expenditure incurred by a firm or producer to purchase or hire factors of production in order to produce a product.
OPPORTUNITY COST
Opportunity Cost can be defined as the value of next best alternative foregone. It is a common practice that a person makes a list of several activities before adopting a particular one to pursue his/her goal. Similarly, in production a producer leaves some alternatives before finally choosing to produce the particular output. So, while finally choosing one, the producer did forego the alternative production.
Let us take example of a farmer. He can produce either rice or wheat on a piece of land. If he has decided to produce wheat on this piece of land, he has to forego the production of rice for producing wheat. So, value of rice foregone (next best alternative) is the opportunity cost of producing wheat.
FACTORS OF PRODUCTION
Resources or inputs that are used in the production process to produce output (i.e.), finished goods and services are known as factors of production. These are:
- LAND
- LABOUR
- CAPITAL
- ENTREPRENEUR
The income that resource owners earn in return for land resources is called RENT
Labour is ability to work or human factor of production. The income earned by labour resources is called Wages and is the largest source of income for most people.
Capital is part of wealth which is used for production. The process of production of new Capital Goods, Plants & Equipment is called as INVESTMENT & this investment with a view to obtain the target returns over a specific period of time. The income earned by owners of Capital is called Interest.
Capital does not solely in physical form and it also includes the intellectual discoveries like computer software, formula for Medicine, etc.
Note: Money becomes Capital only when it is used to purchase real Capital goods like, Plant, Machinery, etc.
An Entrepreneur is a person who combines the other factors of productions like Land, Labour And Capital to earn a profit.
Good and services are the final output of the process of production.
The input and output of factors of production and given below:
INPUT | OUTPUT |
Land | Rent |
Labour | Wages |
Capital | Interest |
Entrepreneurship | Profit |
CONCEPT OF NATIONAL INCOME
The output of an economy is the monetary value of final goods and services in a given time period. The output of an economy also consists of production of machines which are consumed every year, and hence is called depreciation. The output is also classified as those produced within the geographic boundary of the country known as domestic output.
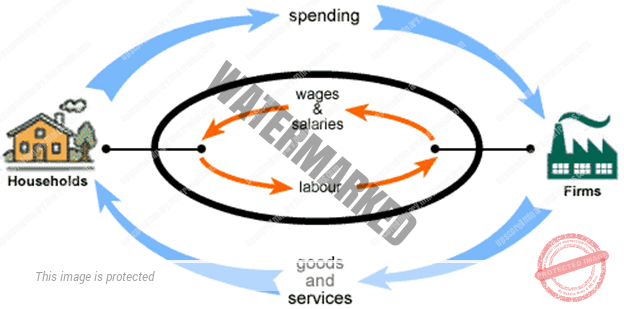
In an economy, Households Buy Goods And Services from firms, and firms use their revenue from sales to pay wages to workers, rent to landowners, and profit to firm owners.
SIGNIFICANCE OF NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING
Income level is the most commonly used tool to determine the well-being and happiness of nations and their citizens. National Income data are significant for a country’s per capita income which reflects the economic welfare of the country. It also paves way
- To find the total value of economic activities and output in the country.
- To find out the level of economic development of a country.
- It helps the business to plan for production.
- For policy formulation by State.
Hence keeping these concepts in account the National income accounting consist of broadly four concepts:
- GDP
- NDP
- GNP
- NNP
தேசிய வருவாய் – 1
பொருளாதார செல்வம் அல்லது ஒரு நாட்டின் நல்வாழ்வு வளங்களை வைத்திருப்பதை மட்டும் சார்ந்தது அல்ல, சுவை உற்பத்தி மற்றும் விநியோக மற்றும் அதன் விளைவாக வரும் வருமானம் மற்றும் செல்வத்தை உருவாக்க பயன்படுகிறது. எனவே உற்பத்தியின் ஓட்டத்தை உருவாக்க குறிப்பிட்ட சமூக மற்றும் தொழில்நுட்ப கட்டமைப்பிற்குள் மக்கள் இயற்கை மற்றும் மனிதனால் உருவாக்கப்பட்ட சூழலுடன் ஆற்றல்களை இணைக்கின்றன. நவீன பொருளாதாரங்களில் இந்த உற்பத்தி ஓட்டம் அந்த பொருளாதாரம் தனிநபர்கள் மற்றும் நிறுவனங்களால் உற்பத்தி செய்யப்படும் பொருள் மற்றும் சேவைகளாக மொழிபெயர்க்கப்பட்டுள்ளது.
எனவே, ஒரு பொருளாதாரத்தில் உற்பத்தி செய்யப்படும் பொருட்கள் மற்றும் சேவைகளின் அடிப்படையில் உருவாக்கப்பட்ட எந்த செல்வத்தின் அளவீடு மற்றும் கணக்கு தேசிய வருமானம் மற்றும் அதன் கணக்கியல் செயல்முறை ஆகும். இந்த அத்தியாயம் நம் தேசிய வருமானத்தில் அடிப்படைக் கருத்துக்களை மற்றும் விதிமுறைகள் அதன் மதிப்பீடு முறைகளைப் பார்ப்போம்.
சந்தை
சந்தை என்பது பொருட்கள் மற்றும் சேவைகளை வாங்கும் மற்றும் விற்பனை செய்யும் இடமாகும். சண்டைகள் இரண்டு முக்கிய பங்கேற்பாளர்களை சார்ந்துள்ளது, அதாவது வாங்குபவர்கள் மற்றும் விற்பவர்கள்
- இயற்பியல் இடைவேளை கொண்ட சண்டை:
பொருட்கள் மற்றும் சேவைகள் பரிவர்த்தனையை மேற்கொள்வதற்காக வாங்குபவர்களும் விற்பவர்களும் ஒன்றாக சந்திக்கிறார்கள்
- இயற்பியல் இடைவெளி இல்லா சந்தை: எடுத்துக்காட்டு பங்குசந்தை
இங்கே வாங்குபவர்கள் மற்றும் விற்பவர்கள் ஒருவருக்கொருவர் நேரடியாக தொடர்பு கொள்வதில்லை.
வழங்கள் மற்றும் தேவையின் விதி
எண்ணிக்கை விற்கப்படும் பொருட்களின் அல்லது சேவையின் விலையில் நேரடி தாக்கம் கொண்டிருக்கும் மேலும் இது வழங்கல் மற்றும் தேவைக்கான சட்டம் என்று அழைக்கப்படுகிறது.
வழங்கல் மற்றும் தேவை உறவுமுறை
ஒரு குறிப்பிட்ட பொருளுக்கு வாங்குபவர்களை விட அதிக விற்பனையாளர்கள் இருந்தால், குறைந்த தேவை காரணமாக பொருட்களின் விலை குறையும்.
ஒரு குறிப்பிட்ட பொருளுக்கு விற்பவர்களை விட அதிக வழங்குபவர்கள் இருந்தாள் அதிக தேவை காரணமாக பொருட்களின் விலை அதிகரிக்கும்.
தேவை
“…..தேவை என்பது பொருட்கள் அல்லது சேவையின் அளவை குறைக்கிறது, வீடு வாங்குபவர்கள் குறிப்பிட்ட விலையில் விரும்பப்படுகிறது, மற்ற அனைத்தும் மாறாமல்….. “
எடுத்துக்காட்டு, 100 வாலி தக்காளி ஒவ்வொரு மாதமும் ஒரு குறிப்பிட்ட நகரத்தில் ஒரு வாலிக்கு ரூபாய் 50 என்ற விலையில் விற்கப்படுகிறது, அந்த அளவு 100 வாலி தக்காளி மாதத்திற்கு 50 விகிதம் கேட்கப்படுகிறது. விலை ரூபாய் 60 என்றால் நாம் அளவை எதிர்பார்க்கலாம்.
குறைவாக இருக்க வேண்டும் என்று கோரப்பட்டது. விலை ரூபாய் 40 ஆக இருந்தாள் கோரப்பட்ட அளவு அதிகமாக இருக்கும் என்று நாங்கள் எதிர்பார்க்கிறோம்.
விநியோகம்
வினியோகம் என்பது ஒரு அடிப்படை பொருளாதாரம் இது நுகர்வோருக்கு கிடைக்கும் ஒரு குறிப்பிட்ட பொருள் அல்லது சேவையின் மொத்த அளவை விவரிக்கிறது. ஒரு குறிப்பிட்ட விலையை பெறும்போது உற்பத்தியாளர்கள் வழங்க விரும்பும் ஒரு குறிப்பிட்ட பொருளின் அளவையும் இது குறைக்கிறது இது பொருட்களின் உற்பத்தியை பொறுத்தது.
செலவு
ஒரு பொருளை உற்பத்தி செய்வதற்காக ஒரு நிறுவனமும் அல்லது தயாரிப்பாளரோ உற்பத்தி காரணிகளை வழங்குவதற்கு அல்லது பணி அமர்த்துவதற்கு செய்யப்படும் செலவு, செலவு என வரையறுக்கப்படுகிறது.
வாய்ப்பு செலவு
வாய்ப்புக்கான செலவை அடுத்த சிறந்த மாற்று முன்கூட்டியே மதிப்பாக வரையறுக்கலாம். ஒரு நபர் தனது குறிக்கோளை தொடர ஒரு குறிப்பிட்ட செயலை செய்வதற்கு முன் பல செயல்பாடுகளில் பட்டியலை உருவாக்குவது பொதுவான நடைமுறையாகும். அதேபோல் உற்பத்தியில் ஒரு தயாரிப்பாளர் குறிப்பிட்ட வெளியிட்ட உற்பத்தி செய்வதற்கு முன்பு சில மாற்றங்களை விட்டுவிடுகிறார். எனவே, இறுதியாக ஒன்றை தேர்ந்தெடுக்கும்போது தயாரிப்பாளர் மாற்று உற்பத்தியை கைவிட்டார்
ஒரு விவசாயி உதாரணத்தை எடுத்துக் கொள்வோம். அவர் ஒரு துண்டு நிலத்தில் அரிசி அல்லது கோதுமை உற்பத்தி செய்யலாம். இந்த நிலத்தில் கோதுமையை உற்பத்தி செய்ய அவர் முடிவு செய்திருந்தாள் கோதுமை உற்பத்திக்கு அரிசி உற்பத்தியை அவர் கைவிட வேண்டும் எனவே அரிசி முன்கூட்டியே மதிப்பு (அடுத்த சிறந்த மாற்று) கோதுமை உற்பத்தி வாய்ப்பு ஆகும்.
உற்பத்திக்கான காரணிகள்
வெளியீட்டை உற்பத்தி செய்வதற்கு உற்பத்தி செயல்பாட்டில் பயன்படுத்தப்படும் வழங்கல் அல்லது உள்ளீடுகள் அதாவது முடிக்கப்பட்ட பொருள்கள் மற்றும் உற்பத்தி காரணிகளாக அறியப்படுகின்றன. இவை:
- நிலம்
- தொழிலாளர்
- மூலதனம்
- முதலாளி
நில வளங்களுக்கு ஈடாக உரிமையாளர்கள் சம்பளத்துக்கு வருமானம் வாடகை என்று அழைக்கப்படுகிறது.
உழைப்பு என்பது வேலை செய்யும் திறன் அல்லது உற்பத்தியின் மனித காரணி. தொழிலாளர் வளங்களுக்கு கிடைக்கும் வருமானம் கூலி என்று அழைக்கப்படுகிறது மற்றும் பெரும்பாலான மக்களுக்கு மிகப் பெரிய வருமானம் ஆதாரமாக உள்ளது.
மூலதனம் என்பது செலவின் ஒரு பகுதியாகும், இது உற்பத்திக்கு பயன்படுத்தப்படுகிறது. புதிய மூலதன பொருட்கள், இடங்கள் மற்றும் உபகரணங்கள் உற்பத்தி செயல்முறை முதலீடு என்று அழைக்கப்படுகிறது மற்றும் குறிப்பிட்ட காலப்பகுதியில் வருமானத்தை பெறும் நோக்கில் இந்த முதலீடு உள்ளது. மூலதனத்தின் உரிமையாளர்களால் இடப்பட்ட வருமானம் வட்டி என்று அழைக்கப்படுகிறது.
மூலதனம் வெறும் உடல் வடிவத்தில் மட்டுமல்ல அது கணினி மென்பொருள் மருத்துவத்திற்கான சூத்திரம் போன்ற அறிவார்ந்த கண்டுபிடிப்புகளையும் உள்ளடக்கியது.
குறிப்பு: ஆலை, எந்திரம் போன்ற உண்மையான மூலதன பொருட்களை வாங்கும்போது மட்டுமே பணம் மூலதனமாகிறது.
ஒரு தொழில் முனைவோர் என்பது நிலம் தொழிலாளர் மற்றும் மூலதனம் போன்ற உற்பத்திகளின் பிற காரணிகளை இணைத்து லாபம் சம்பாதிப்பவர் என்பதாகும்.
சரக்கு மற்றும் சேவைகள் உற்பத்தி செயல்முறை இன் இறுதி வெளியீட்டு.
தேசிய வருமானத்தின் விளக்கம்
ஒரு பொருளாதாரத்தின் வெளியீடு என்பது ஒரு குறிப்பிட்ட காலப்பகுதியில் இறுதி பொருட்கள் மற்றும் சேவைகளின் பண மதிப்பு ஆகும். ஒரு பொருளாதாரத்தின் வெளியீடு ஒவ்வொரு ஆண்டு நுகரப்படும் எந்திரங்களின் உற்பத்தியையும் கொண்டுள்ளது எனவே இது தேய்மானம் என்று அழைக்கப்படுகிறது. வெளியீடு உள்நாட்டு வெளியீடு எனப்படும் நாட்டின் புவியியல் எல்லைக்குள் உற்பத்தி செய்யப்பட்டவை என வகைப்படுத்தப்படுகிறது.
ஒரு பொருளாதாரத்தில், குடும்பங்கள் நிறுவனங்களிலிருந்து பொருட்கள் மற்றும் சேவைகள் வாங்குகின்றன மேலும் நிறுவனங்கள் விற்பனையில் இருந்து கிடைக்கும் வருவாயை தொழிலாளர்களுக்கு ஊதியம் உரிமைகளுக்கு வாடகை மற்றும் நிறுவன உரிமையாளர்கள் லாபம் ஆகியவற்றை பயன்படுத்துகின்றனர்.
தேசிய வருமான கணக்கு முக்கியத்துவம்
நாடுகள் மற்றும் நாட்டின் குடிமக்களின் நல்வாழ்வு மற்றும் மகிழ்ச்சியை தீர்மானிக்க பொதுவாக பயன்படுத்தப்படும் கருவியாக வருமான நிலை உள்ளது. நாட்டின் பொருளாதார நலனை பிரதிபலிக்கும் ஒரு நாட்டின் தனிநபர் வருமானத்திற்கு தேசிய வருமான தரவு முக்கியமானது. அதுவும் வழிவகுக்கிறது.
- நாட்டின் பொருளாதார நடவடிக்கைகள் மற்றும் வெளி நாட்டின் மொத்த மதிப்பை கண்டறிய உதவுகிறது.
- ஒரு நாட்டின் பொருளாதார வளர்ச்சியின் அளவை அறிய உதவுகிறது.
- இது உற்பத்தியை திட்டமிடுவதற்கு வணிகத்திற்கு உதவுகிறது.
- மாநிலத்தின் கொள்கை உருவாக்கம்.
எனவே இந்த கருத்துக்களை கணக்கில்கொண்டு தேசிய வருமான கணக்கியல் பரந்த நான்கு கருத்துக்களை கொண்டுள்ளது
- மொத்த உள்நாட்டு உற்பத்தி
- நிகர உள்நாட்டு உற்பத்தி
- மொத்த நாட்டின் உற்பத்தி
நிகர நாட்டின் உற்பத்தி
