- VALUES OF BIODIVERSITY
- MAJOR THREATS OF THE BIODIVERSITY
- SPECIES EXTINCTION
- BIO PIRACY
UNIT 2 – BIODIVERSITY– PART 4
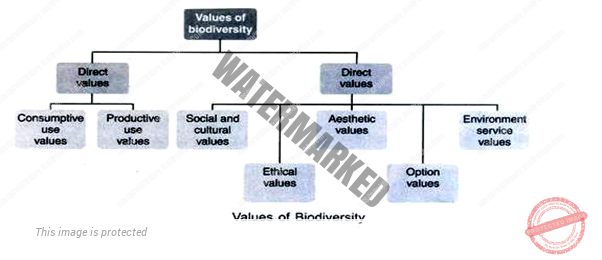
VALUES OF BIODIVERSITY
Biodiversity is the most precious gift of nature mankind is blessed with. As all the organisms in an ecosystem are interlinked and interdependent, the value of biodiversity in the life of all the organisms including humans is enormous. Firstly Biodiversity is directly used as a source for food, fibre, fuel and other extractable resources. Secondly, biodiversity plays an important role in ecosystem processes providing the regulating, cultural and supporting services.
ECOLOGICAL VALUE:
Biological diversity is also essential for preserving ecological processes, such as fixing and re- cycling of nutrients, soil formation, circulation and cleansing of air and water, global life support (plants absorb CO2, give out O2), maintaining stream and river flows throughout the year, erosion control and local flood reduction.
CONSUMPTIVE USE VALUE
The direct utilisation of timber, food, fuel wood, fodder by local communities. The biodiversity held in the ecosystem provides forest dwellers with all their daily needs, food, building material, fodder, medicines and a variety of other products. They know the qualities and different uses of wood from different species of trees, and collect a large number of local fruits, roots and plant material that they use as food, construction material or medicines. Fisher folk are highly dependent on fish and know where and how to catch fish and other edible aquatic animals and plants.
PRODUCTIVE USE VALUE
Marketable goods such as timber are available. It is the raw material from which new drugs can be identified from plant or animal products. Preservation of biodiversity has now become essential for industrial growth and economic development.
A variety of industries such as pharmaceuticals are highly dependent on identifying compounds of great economic value from the wide variety of wild species of plants located in undisturbed natural forests. This is called bio- logical prospecting.
ETHICAL AND MORAL VALUES
Ethical values related to biodiversity conservation are based on the importance of protecting all forms of life. Tribal people in our country We have in our country a large number of sacred groves or ‘deorais’ pre- served by in several States. These sacred groves around ancient sacred sites and temples act as gene banks of wild plants.
MAJOR THREATS TO THE BIODIVERSITY
Any sort of change incurred by natural or anthropogenic activities in the local environmental conditions may pose a threat to the plant/ animal/ microbial diversity sustaining there. In fact, the habitat degradation and fragmentation, caused by human-induced land use changes is the main factor driving biodiversity loss.
World Wide Fund (WWF) report suggests that 52% of the world’s biodiversity (including terrestrial, freshwater and marine diversity) has been lost in a 40 year span between 1970 and 2010, freshwater diversity being affected most.
Activities such as Urbanization, Expansion of Agricultural Lands, Industrialization, Deforestation, Mining, Damming and Dredging Of Rivers, And Draining Of Wetlands, Estuaries and mangroves are majorly responsible for turning a habitat unsuitable for the local species.
THREATS & THEIR CAUSES.
Threats to biodiversity in terrestrial ecosystems
| Underlying causes
|
Habitat degradation and fragmentation
| Deforestation, Urbanization, industrialization, expansion of agricultural lands and extension of road network, invasion in wild areas for recreation and tourism
|
Dynamic relationship between agriculture and wildlife
| Modernization of agricultural practices and disappearance of natural hosts of wildlife such as hedges, trees, ponds, etc.
|
Pollution
| Population explosion, Industrialization, increased number of vehicles, use of excessive fertilizers in agricultural practices, unhealthy waste management techniques etc.
|
Invasions by alien species
| International trade and transport, use of exotic plant species in gardening and forestry, introduction of exotic species for hybridization, climate change.
|
Epidemics
| Introduction of exotic pests, pollution and habitat destruction
|
Climate change
| Emissions of greenhouse gases, deforestation and other land use changes due to human activities
|
Desiccation of soils and wetlands
| Overuse of underground water tables
|
Poaching | High value of animal products in black market, usage of animal products in traditional medicines in southeast Asia and china |
SPECIES EXTINCTION
It is estimated that more than 99.9% of all species that had ever lived on this planet earth have gone extinct. Out of the rest, 0.1% of extant species (species that are living today) which is currently estimated to be around 1 trillion, we know only one thousandth of one percentage of this, indicating extreme knowledge gap.
It is now estimated that almost half of all extant species will go extinct by 2100 even before these species are discovered and characterized. Extinction, or more specifically ‘species extinction,’ refers the death of the last member of a species.
Kinds of Species vulnerable to extinction:
- Rare species (as listed by IUCN)
- Species with restricted geographical range (such as the organisms dwelling on the island ecosystems)
- Species occurring at the sites of high human disturbance/ exploitation
- Species with large/ specialized/ stable habitat requirements
- Species with slow reproductive rate
- Species being heavily predated
- Seasonal migrants
- Species with lesser genetic variability
- Species with no prior contact with humans
- Species closely related to the extinct or threatened species
HIPPO, OR THE SIXTH MASS EXTINCTION:
HIPPO stands for Habitat Loss and Destruction, Invasive Species, Pollution, Human Population, and Overharvesting. Because of human population expansion and agriculture, a number of pristine habitats have now completely altered. Habitat loss is especially prone in the wetland ecosystems of the world, and a number of endemic species of the wetlands have become extinct. There are at least 784 confirmed species extinctions since 1500s. The main causes of this event can be summarized in the acronym HIPPO.
BIO PIRACY
Definition:
Bio piracy is the practice of commercially exploiting naturally occurring genetic material or biochemical. Most of the indigenous people possess a traditional knowledge that mainly comprises of genetic diversity and biological feature of the natural environment from generation to generation. Some of the traditional knowledge that is relevant to global survival includes the following components.
- Medicinal Plants.
- Farming or Agriculture.
- Varieties of Food crops.