- WASTE MANAGEMENT TECHNIQUES AND PRACTICES
UNIT 4 – ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION – PART 14
4.6.2. WASTE MANAGEMENT TECHNIQUES AND PRACTICES
62 million tonnes of waste is generated annually in the country at present, out of which 5.6 million tonnes is plastic waste, 0.17 million tonnes is biomedical waste, hazardous waste generation is 7.90 million tonnes per annum and 15 lakh tons is e-waste. He added that the per capita waste generation in Indian cities ranges from 200 grams to 600 grams per day. Shri Javadekar underlined the fact that 43 million TPA is collected, 11.9 million is treated and 31 million is dumped in landfill sites, which means that only about 75-80% of the municipal waste gets collected and only 22-28 % of this waste is processed and treated. “Waste generation will increase from 62 million tonnes to about165 million tonnes in 2030.
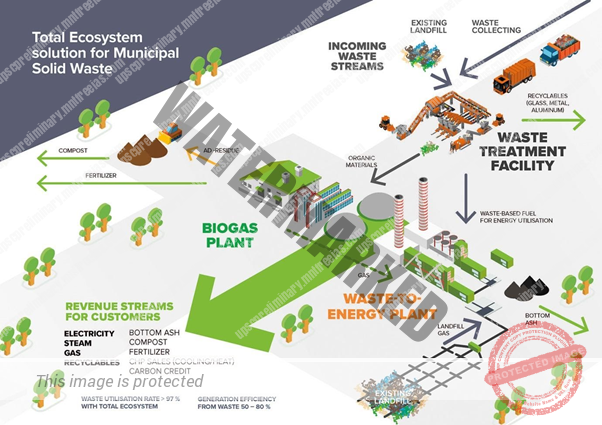
Waste management or Waste disposal is all the activities and actions required to manage waste from its inception to its final disposal. This includes amongst other things, collection, transport, treatment, and disposal of waste together with monitoring and regulation. It also encompasses the legal and regulatory framework that relates to waste management encompassing guidance on recycling etc.
- Landfills – Throwing daily waste/garbage in the landfills is the most popularly used method of waste disposal used today. This process of waste disposal focuses attention on burying the waste in the land. Landfills are commonly found in developing countries. It is one of the simplest and most widely followed techniques but has huge environmental burden. Reducing urban spaces and landfills ending up as hills beyond their capacity is posing serious threat to the local ecosystem. Mostly in urban areas, water bodies are converted into landfills and it is adding to the water shortage problem.
- Incineration or combustion is a type disposal method in which municipal solid wastes are burned at high temperatures so as to convert them into residue and gaseous products. The biggest advantage of this type of method is that it can reduce the volume of solid waste to 20 to 30 percent of the original volume, decreases the space they take up and reduce the stress on landfills. This process is also known as thermal treatment where solid waste materials are converted by Incinerators into heat, gas, steam and ash.
- Composting is a natural process where organic wastes break down into nutrient-rich compost perfect for your garden plants. Microbes decompose the organic materials as they sit in a compost pile or bin for months. Composting preserves more nutrients than incineration and is the preferred method for organic waste disposal.
4. Faecal sludge management (FSM) – is the slurry that contains both solid and liquid waste that accumulates in onsite sanitation systems (OSS) e.g. septic tanks. It is raw or partially digested slurry that results from the collection, storage or treatment of combinations of excreta and black water, with or without grey water. This has three main components – scum, effluent and sludge. It has an offensive odour, appearance and contains significant levels of grease, grit, hair, debris and pathogenic microorganisms. FSM involves collection, treatment and proper disposal/ reuse. Efficient faecal sludge (septage) management include safe disposal of the treated septage. |
- WASTE TO ENERGY (WtE) process involves converting of non-recyclable waste items into useable heat, electricity, or fuel through a variety of processes. This type of source of energy is a renewable energy source as non-recyclable waste can be used over and over again to create energy.
- PYROLYSIS – Pyrolysis is defined as a process in which the organic waste is thermally degraded in the absence of oxygen to produce products like char, oil and combustible gases. Pyrolysis transforms low-energy density waste to bio-fuels of high-energy density and other high value chemicals. Pyrolysis is a waste to energy process where waste is converted into valuable products.
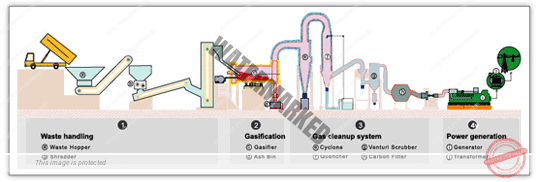
- GASIFICATION – Gasification is a process by which the solid and liquid waste materials are converted by the action of heat into gaseous material, ash and tar in the presence of limited supply of oxygen.
It is a unique process 4 Environmental Sciences Solid and Hazardous Waste Management Advanced Thermal Treatment Technologies – Gasification by which the carbon in the municipal solid waste is converted into energy without burning them.
The gases generated include carbon monoxide and hydrogen termed popularly as ‘syngas’. Other gases include carbon dioxide and methane. Air, pure oxygen and steam are used for gasification. Gasification occurs in a wide range of temperature (i.e.) 800 – 1400 ⁰C.