- INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS
- MITIGATION
- NOISE POLLUTION
UNIT 4 – ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION – PART 6
- INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS
The 2005 World Health Organization’s “WHO Air quality guidelines” offer global guidance on thresholds and limits for 4 key air pollutants that pose health risks – particulate matter (PM), ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and sulfur dioxide (SO2).
Guideline values prescribed by WHO are
PM 2.5 | 10 μg/m3 annual mean |
PM 10 | 20 μg/m3 annual mean |
O3 | 100 μg/m3 8-hour mean |
NO2 | 40 μg/m3 annual mean |
SO2 | 20 μg/m3 24-hour mean |
The WHO Guidelines indicate that by reducing particulate matter (PM10) pollution from 70 to 20 micrograms per cubic meter (μg/m), air pollution-related deaths can be cut by around 15In%. Indian Standards are slightly less stringent as compared to WHO guidelines. However, the world’s average PM10 levels by region range from 26 to 208 μg/m3, with a world’s average of 71 μg/m3 as per WHO estimates published in 2014.
MITIGATION
Air pollution control devices are a series of devices that work to prevent a variety of different pollutants, both gaseous and solid, from entering the atmosphere primarily out of industrial smokestacks. These control devices can be separated into two broad categories – devices that control the amount of particulate matter escaping into the environment and devices that control acidic gas emissions.
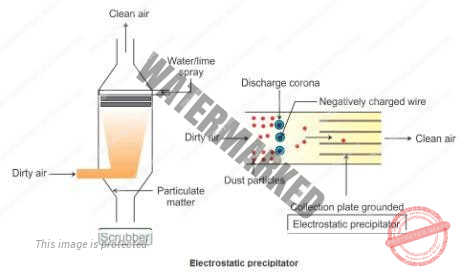
- Electrostatic precipitatoris a type of filter that uses static electricity to remove soot and ash from exhaust fumes before they exit the smokestacks. Unburned particles of carbon in smoke are pulled out of the smoke by using static electricity in the precipitators, leaving clean, hot air to escape the smokestacks.
This unreacted carbon can affect respiratory system.
- SCRUBBER – are a type of system that is used to remove harmful materials from industrial exhaust gases before they are released into the environment. It is used to specifically remove SOx it is referred to as flue gas desulfurization. There are two main types of scrubbers, Wet Scrubbers And Dry Scrubbers. The main difference is in the type of material used to remove the gases. By removing acidic gases from the exhaust before it is released into the sky, scrubbers help prevent the formation of acid rain.
- INCINERATION – Incinerationis used to convert VOC emissions into carbon dioxide and water through combustion. The incineration generally takes place in a specialized piece of equipment known as an afterburner, which is built to create the conditions necessary for complete combustion (such as sufficient burn time and a high temperature). Additionally, the incinerated gas must be mixed to ensure complete combustion.
- CARBON CAPTURE – Carbon capture and storagerefers to the process of capturing this carbon dioxide and storing it below ground, pumping it into geologic layers. This process is rarely being used, but is talked about extensively as a way to limit greenhouse gas emissions leading to climate change.
- Catalytic converteris an exhaust emission control device that reduces toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalysing a redox reaction (an oxidation and a reduction reaction). They are also used on some wood stoves to control emissions.
Additionally other measures like reducing pollution by sustainable consumption means, deforestation, increasing carbon sinks etc is required.
NOISE POLLUTION
Noise pollution is generally defined as regular exposure to elevated sound levels that may lead to adverse effects in humans or other living organisms. According to the World Health Organization, sound levels less than 70 dB are not damaging to living organisms, regardless of how long or consistent the exposure is. Exposure for more than 8 hours to constant noise beyond 85 dB may be hazardous.
SOURCES
- Street Traffic Sounds From Cars, Buses, Pedestrians, Ambulances Etc.
- Construction Sounds Like Drilling Or Other Heavy Machinery In Operation.
- Airports, With Constant Elevated Sounds from Air Traffic, I.E. Planes Taking Off or Landing
- Workplace Sounds, Often Common in Open-Space Offices
- Constant Loud Music in Or Near Commercial Venues
- Industrial Sounds Like Fans, Generators, Compressor, Mills Train Stations Traffic
- Household Sounds, From the Television Set To Music Playing On The Stereo Or Computer, Vacuum Cleaners, Fans And Coolers, Washing Machines, Dishwashers, Lawnmowers
- Events Involving Fireworks, Firecrackers, Loudspeakers
- Conflicts Generate Noise Pollution Through Explosions, Gunfire Etc. The Dysfunctions, In This Case, Are Likely Caused By The Conflict And Insecurity And Less By The Noise Pollution In Itself, Although That Compounds Stress Levels Too.
4.3.2. Impact of Noise Pollution
- Human health
- HYPERTENSIONis, in this case, a direct result of noise pollution caused elevated blood levels for a longer period of time.
- Hearing losscan be directly caused by noise pollution, whether listening to loud music in your headphones or being exposed to loud drilling noises at work, heavy air or land traffic, or separate incidents in which noise levels reach dangerous intervals, such as around140 dB for adult or 120 dB for children.
- SLEEP DISTURBANCESare usually caused by constant air or land traffic at night, and they are a serious condition in that they can affect everyday performance and lead to serious diseases.
- Child development. Children appear to be more sensitive to noise pollution, and a number of noise-pollution-related diseases and dysfunctions are known to affect children, from hearing impairment to psychological and physical effects. Also, children who regularly use music players at high volumes are at risk of developing hearing dysfunctions. In 2001, it was estimated that 12.5% of American children between the ages of 6 to 19 years had impaired hearing in one or both ears
- Cardiovascular dysfunctions Elevated blood pressure caused by noise pollution, especially during the night, can lead to various cardiovascular diseases.
- Dementiaisn’t necessarily caused by noise pollution, but its onset can be favoured or compounded by noise pollution.
- Psychological dysfunctionsand noise annoyance. Noise annoyance is, in fact, a recognized name for an emotional reaction that can have an immediate impact.