- WATER POLLUTION
- POLLUTANTS OF WATER
UNIT 4 – ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION – PART 8
WATER POLLUTION
Water is distributed in nature in different forms, such as rainwater, river water, spring water and underground in aquifers. Rainwater is the purest form of naturally occurring water.
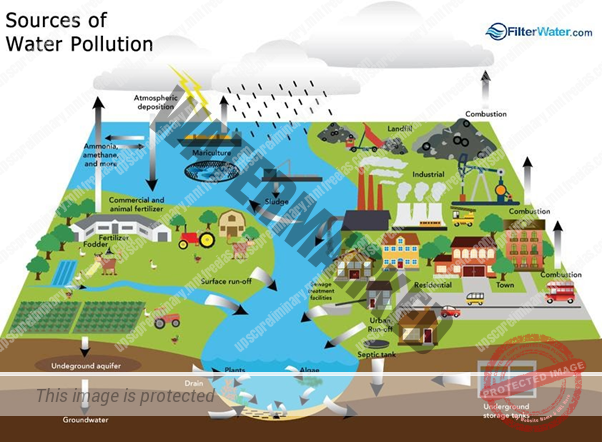
Water pollution is the contamination of natural water present in lakes, rivers, streams, oceans, and groundwater due to inflow or deposition of pollutants directly or indirectly into the water systems. Any modifications or change in the chemical, physical and biological properties of water that can cause any harmful consequences on living things and the environment is known as water pollution.
Water pollution is very often caused by human activities. In most of the developing countries the major cause of death is consumption of polluted water. Water pollution affects all living species, populations and the complete functioning of the ecosystem that lives in the waters and affects the survival of live on this planet.
POLLUTANTS OF WATER
Water pollutants can be divided into four major categories- Chemical, Physical, Physiological and Biological. Though the physical and physiological pollutions are mainly outcomes of chemical pollutants, they are categorized separately because of their nature.
- Chemical Pollutants: Chemical pollutants can further be divided into Organic pollutants and Inorganic pollutants
- Organic pollutants: Organic pollutants are the compounds those contain carbon atom in them and mainly of biological origin. These are the oxygen depleting substances in water.
- They are carried to the water course from different sources like Sewage, Animal And Human Excreta, Refineries, Distillery, Pulp And Paper Industry, Tanneries, Diary Industry, Textile Industry, Slaughter Houses BOD and COD is common indicator of high organic content of waste water. The organic pollutants could be further subdivided into two.
BIODEGRADABLE ORGANIC POLLUTANTS | NON-BIODEGRADABLE ORGANIC POLLUTANTS |
Proteins, Fats, Carbohydrates, Alcohols, acids, aldehydes, esters, soaps etc. | Pesticides (DDT, aldrin, dieldrin, endrin, endosulfan, lindane, toxaphene, mirex, heptachlor etc.), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB’s), polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAH’s), plastics, dioxins, furans, phenols, dyes, detergents etc. |
BOD & COD (a measure of water pollution)
COD or Chemical Oxygen Demand is the total measurement of all chemicals (organics & in-organics) in the water / wastewater. BOD is a measure of, the amount of oxygen that requires for the bacteria to degrade the organic components present in water / wastewater.
Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) is the amount of dissolved oxygen needed (i.e. demanded) by aerobic biological organisms to break down organic material present in a given water sample at certain temperature over a specific time period. The BOD value is most commonly expressed in milligrams of oxygen consumed per litre of sample during 5 days of incubation at 20 °C and is often used as a surrogate of the degree of Organic Pollution Of Water.
BOD reduction is used as a gauge of the effectiveness of wastewater treatment plants. BOD of wastewater effluents is used to indicate the short-term impact on the oxygen levels of the receiving water.
Inorganic pollutants: Inorganic pollutants include inorganic acids, alkalis, salts, anions, cations, free chlorine, ammonia etc. They are added a result of industrial effluents, sewage, household cleansers and surface run-off from urban and agricultural field etc. They affect the physical and chemical quality of water.
Common inorganic pollutants found in water Pollutant are:
- Acids – Phosphoric ACID, SULFURIC ACID, HYDROCHLORIC ACIDS ETC.
- Alkalis – Sodium HYDROXIDE, LIME ETC.
- Cations – Calcium, MAGNESIUM, SODIUM, POTASSIUM, AMMONIUM, IRON, MANGANESE, ALUMINIUM, MERCURY, LEAD ETC.
- Anions– Phosphates, sulphates, chlorides, nitrites, nitrates, cyanides, carbonates, bicarbonates etc.
2.Physical Pollutants: These are the pollutants which deteriorate the physical parameters of water quality. These include:
- Colour: Colour affects the aesthetic value of water body. Harmful colour producing chemical includes various dyes, toxic coloured compounds of iron and chromium etc. Colour is also produced by pigments like that of microalgae.
- Turbidity: Turbidity is due to colloidal particles which do not settle in standing water. It may be due to presence of inert and harmless material like clay or due to presence of chemicals like Hydrated Iron Oxide, Aluminium Hydroxide And Organic Substances Greater turbidity means presence of greater amount of pollutants in water.
- Suspended matter: These are coarse and insoluble matter suspended in water. Natural suspended matters which are not harmful for health include Silt, Clay, Sand And Rock Particles The suspended matter of sewage and industrial origin are particularly harmful to health.
- Radioactivity: Radioactive pollution occurs due to presence of radionuclides. Radioactive elements are naturally present in earth crust particularly in granite rocks and responsible for background radioactivity. It is very low. Problem arises when radionuclides of high radioactivity are released into water by human activities. Some radioactive elements include Plutonium, Uranium, Thorium, Radon, Iodine, Neptunium, Americium, Cesium, Curium, Strontium-90, Radium226, Cesium-137, Phosphorus-32 etc.
- Froth: Froth formation occurs due to presence surfactants like soaps, detergents, fatty acids and saponins these lower the surface tension of water. Blowing agents like gases (e.g. carbon dioxide), baking powder, isocyanate etc. help in foam formation.
3.Biological Pollutants: The biological pollution occurs due to introduction and growth of micro and macro-organisms in water body, which adversely affect the quality of water, human health and ecosystem. Various biological pollutants include bacteria, algae, weeds, viruses, protozoa, and worms. Some common biological pollutants examples
- BACTERIA – E. coli, Salmonella, S. typhi, Vibrio cholera, Clostridium botulinum etc.
- ALGAE – Various macro and micro algae, some produces toxins Viruses Hepatitis A virus, Poliovirus etc.
- Protozoa – Entamoeba Histolytica, Naegleria Fowleri, Cryptosporidium Parvum, Cyclospora Cayetanensis, Giardia lamblia etc.
- Worms – Round worms, tape worms, flukes etc.
- Weeds – Hydrilla, Potamogeton, Ceratophyllum etc