- EXPLOTATION OF ENERGY RESOURCES AND ITS ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT
- ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT
- SUSTAINABLE RESOURCES FOR THE FUTURE
- SOLAR ENERGY
- APPLICATIONS OF SOLAR ENERGY
UNIT 3 – RESOURCES AND ITS UTILIZATION – PART 13
EXPLOITATION OF ENERGY RESOURCES AND ITS ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT
The use of minerals varies greatly between countries. The greatest use of minerals occurs in developed countries. Like other natural resources, mineral deposits are unevenly distributed around on the earth.
Tin And Copper Mines were necessary for a Bronze Age; Gold, Silver, And Gemstones adorned the wealthy of early civilizations; and iron mining introduced a new age of man. Human wealth basically comes from Agriculture, Manufacturing, And Mineral Resources.
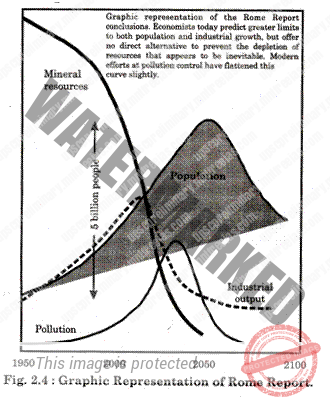
Our complex modern society is built around the exploitation and use of mineral resources. Since the future of humanity depends on mineral resources, we must understand that these resources have limits; our known supply of minerals will be used up early in the third millennium of our calendar.
Furthermore, modern agriculture and the ability to feed an overpopulated world is dependent on mineral resources to construct the machines that till the soil, enrich it with mineral fertilizers, and to transport the products.
We are now reaching limits of reserves for many minerals. Human population growth and increased modern industry are depleting our available resources at increasing rates. The pressure of human growth upon the planet’s resources is a very real problem. The consumption of natural resources proceeded at a phenomenal rate during the past hundred years and population and production increases cannot continue without increasing pollution and depletion of mineral resources. Limits of growth in the world are imposed not as much by pollution as by the depletion of natural resources.
As the industrialized nations of the world continue the Rapid Depletion Of Energy And Mineral Resources, and resource-rich less-developed nations become increasingly aware of the value of their raw materials, resource driven conflicts will increase.
In the figure, we see that by about the middle of the next century the critical factors come together to impose a drastic population reduction by catastrophe. We can avert this only if we embark on a planet-wide program of transition to a new physical, economic, and social world that recognizes limits of growth of both population and resource use.
In a world that has finite mineral resources, exponential growth and expanding consumption is impossible. Fundamental adjustments must be made to the present growth culture to a steady-state system.
This will pose problems in that industrialized nations are already feeling a loss in their standard of living and in non-industrialized nations that feel they have a right to achieve higher standards of living created by industrialization. The population growth continues upward and the supply of resources continues to diminish. With the increasing shortages of many minerals, we have been driven to search for new sources.
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT
The exhaustion of these resources as well as the ill effects of its over utilization is listed below:
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Acid Rain, Global Warming
- Carbon Emissions
- Pollution
- Biodiversity Loss
- Affects Marine Life
- Health Impacts
- Ecosystem Imbalance
The global energy demand is currently met with different types of fossil fuel which are finite and non- renewable in nature. The high energy content and relatively cheaper than renewable energy sources makes fossil fuel consumption in all the energy sectors preferable. The conventional and unconventional fossil fuel reserves are concentrated in small portion of the world. So the judicious utilization of fossil fuel is very essential for meeting energy demands in the future.
Therefore with the given limitation of resources and the problems in its utilization, it is necessary to change faster to better energy consumption techniques, management practices, technologies and usage policies at all levels starting from international efforts narrowing down to individual and locality efforts for energy efficient living.
SUSTAINABLE RESOURCES FOR THE FUTURE
The world is looking for alternate energy sources that can overcome the limitations of fossil fuels. Now a day’s renewable energy plays a very significant role. It gave a chance to us to reduce carbon emissions, clean the air and prevent global warming of planet earth.
The renewable energy is defined by US EPA as the resources that rely on fuel sources that restore themselves over short periods of time and do not diminish. These energy sources are also non – conventional sources of energy.
These include Solar Energy; Wind Energy; Ocean Thermal Power; Wave And Tidal Energy; Geothermal Energy; Hydropower etc. They are capable of solving the twin problems of energy supply in decentralized manner and helping in sustaining cleaner environment.
SOLAR ENERGY
The solar energy is provided by sun by the nuclear fusion reactions. The incident solar energy is not fully utilized for meeting the energy demands at the same time of insolation. The solar energy is generally transformed into thermal or electric energy using solar devices.
The solar energy is, however, the availability of this energy is not fully constant as it is unavailable during night, winter seasons etc. Hence, it is essential to store energy output (Thermal And Electric) from solar devices during High Insolation (in = incident, sol= solar and ation = radiation) from solar device during to meet the thermal and electric load demand during peak demand times which will also exploit the advantage of economies of scale and a reliable source of energy.
APPLICATIONS OF SOLAR ENERGY
Solar energy is converted into thermal energy or electrical energy by the following technologies and is used for various applications.
Flat plate collectors – Among the most common devices used to capture solar energy and convert it to thermal energy are flat-plate collectors, which are used for solar heating applications.
Because the intensity of solar radiation at Earth’s surface is so low, these collectors must be large in area. The most widely used flat-plate collectors consist of a blackened metal plate, covered with one or two sheets of glass, that is heated by the sunlight falling on it.
This heat is then transferred to air or water, called carrier fluids, that flow past the back of the plate. The heat may be used directly, or it may be transferred to another medium for storage. Flat-plate collectors are commonly used for solar water heaters and house heating.
Solar Ponds – Another method of thermal energy conversion is found in solar ponds, which are bodies of salt water designed to collect and store solar energy. The heat extracted from such ponds enables the production of chemicals, food, textiles, and other industrial products and can also be used to warm greenhouses, swimming pools, and livestock buildings. Solar ponds are sometimes used to produce electricity through the use of the organic Rankine cycle engine, a relatively efficient and economical means of solar energy conversion, which is especially useful in remote locations.