- TYPES OF BIOMASS
- CLASSIFICATION OF ENERGY CROPS
- TECHNOLOGIES FOR CONVERSION OF BIOMASS INTO ENERGY
UNIT 3 – RESOURCES AND ITS UTILIZATION – PART 16
TYPES OF BIOMASS
The biomass resources for bio energy production are grouped into
- ENERGY CROPS
- WOODY BIOMASS/FORESTRY AND ITS FORESTRY WASTE: Logs, woods, chips, bark, and leaves are the major forestry waste. Sawdust produced during processing of timber also adds to forest waste.
- AGRICULTURAL RESIDUES – the biomass produced as a by-product of processing, harvesting of agricultural crops are known as agricultural residue. It is classified as
- PRIMARY RESIDUE – The residue produced after harvesting the yield of crop in the field. E.g., Rice Straw, Wheat Straw, Maize Straw, Sugarcane Trash, etc. It is mainly used as animal feed and so less available for energy production in India.
2.SECONDARY RESIDUE – The residue generated during processing. Eg: Rice Husk, Bagasse. These are potential energy sources. The biomass from crop residues is either of dry or wet biomass form. The calorific value, moisture content, fixed carbon content, ash content are important properties in energy generation from the biomass.
- AGRO-INDUSTRIAL WASTE: Paper Mills, Molasses, Pulp Waste from Food Processing Industries, Textile Fibre Waste adds to agro industrial waste
- MUNICIPAL WASTE – The waste collected from household consist mainly the organic portion that can be utilized for energy recovery. Food and kitchen waste, green waste, other biodegradable portion of waste constitutes municipal solid waste. Sewage and animal manure from households also has the energy potential.
- INDUSTRIAL WASTES -The waste and wastewater from the industries like Paper and Pulp Industry, Dairy Industry, Breweries, Vegetable Packaging Industry, Confectionary Industry can also be used as energy resources. The food industry wastes from hotel, restaurants and community kitchens are also a Potential Bio Energy Source. The baggase, a byproduct residue from sugar mills after the juice extraction is used largely for cogeneration to produce electricity.
- CLASSIFICATION OF ENERGY CROPS
Many countries depend upon natural vegetation or crop residues to meet their energy demand. The Bio Energy crops are categorized into
- FIRST GENERATION BIOENERGY CROPS (FGECS): The food crops which are used as energy crops come under this category. It includes Corn, Sugarcane, Oil Palm and Rapeseed. The Fermentation or Trans Etherification processes are used for energy conversion.
- SECOND GENERATION BIOENERGY CROPS (SGECS): These are non-food feedstock. These mainly include Lingo Cellulosic Crops having high energy content than FGECs by means of fermentation or Thermo Chemical Processes.
The examples are perennial forage crops like Switchgrass (Panicumvirgatum), Reed Canary Grass (Phalarisarundinacea L.), Lucerne Or Alfalfa (Medicagosativa L.), Napier Grass (PennisetumpurpureumSchumach.), and Elephant Grass (a hybrid, Miscanthusgiganteus). The non-edible oil crops like Jatrophacurcas L. (30-50% oil) and Soapnut (Sapindusmukorossi and S. Trifoliatus, 52% oil) are also comes under SGECs. It can also include residues from forest products and field crops.
- THIRD GENERATION BIOENERGY CROPS (TGECs): This is based on specially engineered energy crops and algae.
- DEDICATED BIOENERGY CROPS (DECs)- the plant species grown purposefully for energy without compromising on food is known as dedicated energy crops.
THE ENERGY CROPS INCLUDE THE FOLLOWING CELLULOSIC CROPS Eucalyptus (Eucalyptus spp) Poplar (Populus spp.) Willow (Salix spp.) Birch (Betula spp.) Giant reed (Arundodonax) Reed canary grass (Phalarisarundinacea) Switchgrass (Panicumvirgatum) Elephant grass (Miscanthus x gigantus) Johnson grass (Sorghum halepense) Sweet sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) Castor bean (Ricinuscommunis) Physic nut (Jatrophacurcas) Pongamia (Pongamiapinnata) |
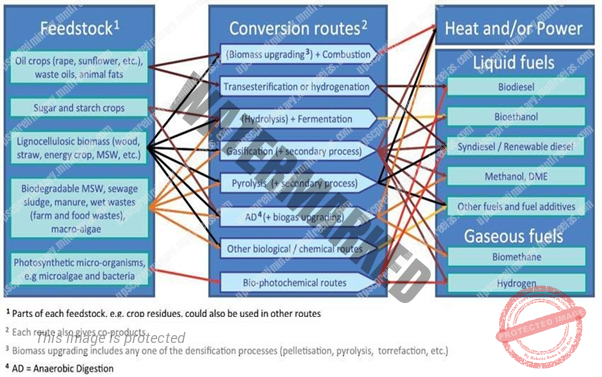
- TECHNOLOGIES FOR CONVERSION OF BIOMASS INTO ENERGY
The conversion technologies from biomass are based on type of biomass (different physical nature and chemical composition of the biomass), and required energy form (Heat, Power, Transport Fuel). The conversion of biomass to energy is mainly by means of
- THERMO-CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGIES – pyrolysis, biomass gasification, combustion, and liquefaction.
- BIO-CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGIES– The fermentation and an-aerobic digestion are the two types of biochemical conversion technologies for biomass to energy.