- CLIMATE
- FACTORS AFFECTING INDIA’S CLIMATE
UNIT 4 – CLIMATOLOGY – PART 12
CLIMATE
CLIMATE refers to the sum total of weather conditions and variations over a large area for a long period of time (more than thirty years).
WEATHER refers to the state of the atmosphere over an area at any point of time.
The elements of Weather and Climate are the same, i.e.
- Temperature
- Atmospheric Pressure
- Wind
- Humidity
- Precipitation
The world is divided into a number of climatic regions. The climate of India is described as the ‘monsoon’ type. This type of climate is found mainly in the south and the Southeast Asia.
CLIMATIC CONTROLS
There are six major controls of the climate of any place. They are Latitude, Altitude, Pressure And Wind System, Distance From The Sea (Continentality), Ocean Currents and relief features.
Due to the curvature of the earth, the amount of solar energy received varies according to latitude. As a result, air temperature decreases from the equator towards the poles. As one goes from the surface of the earth to higher altitudes, the atmosphere becomes less dense and temperature decreases. The hills are therefore cooler during summers. The pressure and wind system of any area depend on the latitude and altitude of the place.
Thus, it influences the Temperature and Rainfall Pattern.
The sea exerts a moderating influence on climate: As the distance from the sea increases, its moderating influence decreases and the people experience extreme weather conditions. This condition is known as Continentality (i.e., very hot during summers and very cold during winters Delhi).
Ocean currents along with onshore winds affect the climate of the coastal areas, For example, any coastal area with warm or cold currents flowing past it, will be warmed or cooled if the winds are onshore.
Relief too plays a major role in determining the climate of a place. High mountains act as barriers for cold or hot winds; they may also cause precipitation if they are high enough and lie in the path of rain-bearing winds. THE LEEWARD SIDE OF MOUNTAINS REMAINS DRY.
FACTORS AFFECTING INDIA’S CLIMATE
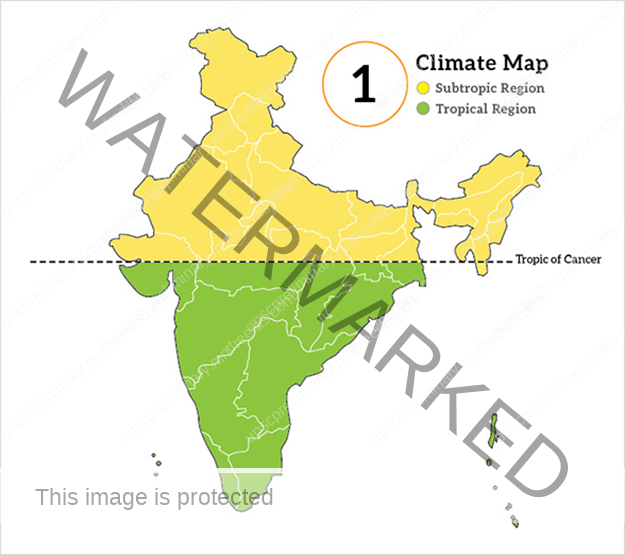
LATITUDE
The Tropic of Cancer passes through the middle of the country from THE RANN OF KUCHCHH in the West To Mizoram in the east.
Almost half of the country, lying south of the Tropic of Cancer, belongs to the tropical area. All the remaining area, north of the Tropic, lies in the sub-tropics. Therefore, India’s climate has characteristics of TROPICAL AS WELL AS SUBTROPICAL CLIMATES.
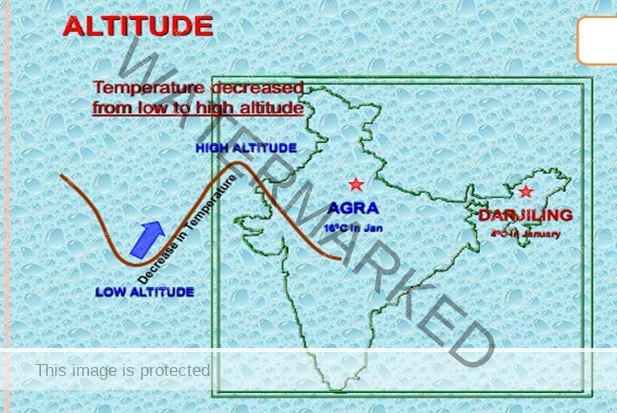
ALTITUDE
India has mountains to the north, which have an average height of about 6,000 metres. India also has a vast coastal area where the maximum elevation is about 30 metres. The Himalayas prevent the cold winds from Central Asia from entering the subcontinent. It is because of these mountains that this subcontinent experiences comparatively milder winters as compared to central Asia.