- ROLE OF IOD & EI NINO AND LINO
- EFFECTS OF EL NINO
- IOD AND INDIAN MONSOON
UNIT 4 – CLIMATOLOGY – PART 19
ROLE OF IOD & EI NO AND LINO
EL NINO
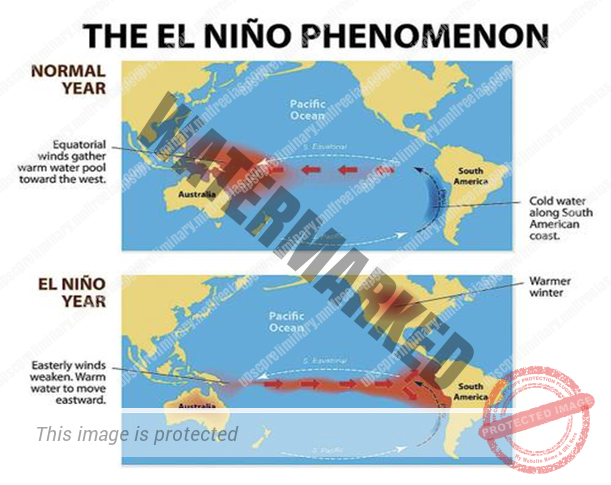
- El Nino refers to the unusual warming of the central and east-central equatorial Pacific Ocean which affects global weather.The warmer waters of the Pacific Ocean cause the winds in various regions to reverse, like the trade winds that come towards India.
- Thischange of wind direction leads to warmer winters and summers and a decrease in rainfall during the monsoon. Most of the time, it also leads to drought.
- There is also an OPPOSITE OF AN EL NIÑO, CALLED LA NIÑA MEANS THE LITTLE GIRL IN SPANISH.This refers to times when waters of the tropical eastern Pacific are colder than normal and trade winds blow more strongly than usual.
- Collectively, El Niño and La Niña are parts of an oscillation in the ocean-atmosphere system called the El Niño-Southern Oscillation, or ENSO cycle.
EFFECTS OF EL NINO
- El Nino affects global weather. Itfavors eastern Pacific hurricanes and tropical storms.
- Recordedunusual rainfall in Peru, Chile, and Ecuador are linked to the climate pattern.
- El Nino reduces the upwelling of cold water, decreasing the uplift of nutrients from the bottom of the ocean. This affects marine life and sea birds. The fishing industry is also affected.
- Drought caused by El Nino can be widespread, affecting southern Africa, India, Southeast Asia, Australia, and the Pacific Islands.Countries dependent on agriculture are affected.
- WHO report on the health consequences of El Nino forecasts a rise in vector-borne diseases,including those spread by mosquitoes, in Central and South America. Cycles of malaria in India are also linked to El Nino.
- Over India, the El Nino has usually been the harbinger of drought and the La Nina of rain
WHAT IS THE INDIAN OCEAN DIPOLE?
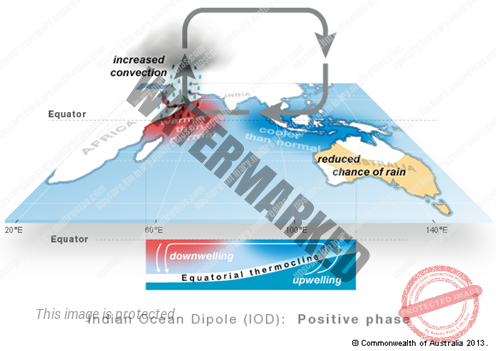
Sustained variations in the difference between tropical western and eastern Indian Ocean surface temperatures are referred to as the Indian Ocean Dipole or IOD.
It is also known as the Indian Niño, is an irregular sea – surface temperature oscillation in which the western Indian Ocean alternately becomes warmer and colder than the eastern part of the ocean.
IOD AND INDIAN MONSOON
The Indian monsoon rainfall is influenced by a system of oscillating sea surface temperatures known as THE INDIAN OCEAN DIPOLE (IOD) in which the western Indian Ocean becomes alternately warmer and then colder than the eastern part of the ocean.
A positive IOD leads to greater monsoon rainfall and more active (above normal rainfall) monsoon.
LOCAL WINDS
Differences in the heating and cooling of earth surfaces and the cycles those develop daily or annually can create several common, local, or regional winds.