- INDIAN CLIMATE – SEASONS
- WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE
UNIT 4 – CLIMATOLOGY – PART 25
INDIAN CLIMATE – SEASONS
- The cold weather season or winter season,
- The hot weather season or summer season,
- The south-west monsoon season or Rainy season, and
- The season of the retreating monsoon or cool season.
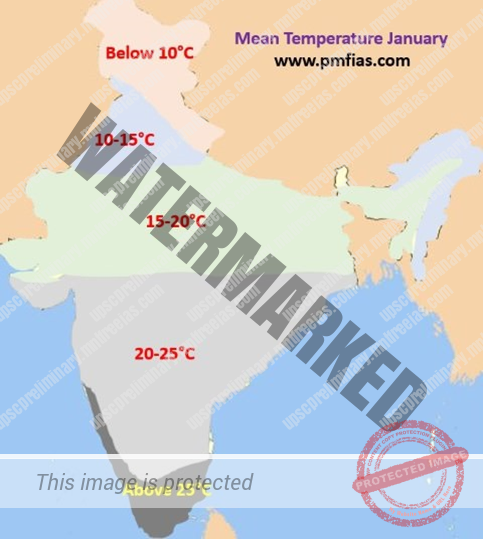
WINTER SEASON IN INDIA
- November – March. Januaryis the coldest month.
- Sun’s apparent path is to the south of equator.
- Clear sky, pleasant weather, low temperature, low humidity, high range of temperature, cool and slow north-east trade winds.
- The diurnal range of temperature, especially in interior parts of the country, is very high.
WESTERN DISTURBANCES IN WINTER SEASON
- They cause light rain in the Indus-Ganga plains and snowfall in the Himalayan belt.
- After the passage of the disturbance, widespread fog and cold waves lowering the minimum temperature by 5° to 10°C below normal are experienced.
- Fog lowers visibility and causes great inconvenience for transportation
TROPICAL CYCLONES IN WINTER SEASON
- This is due to low sea surface temperature and exit of ITCZ farthest south.
- The storms which are born in the Bay of Bengal strike Tamil Nadu and bring heavy rainfall.
- Some of them cross the southern peninsula over to the Arabian Sea.
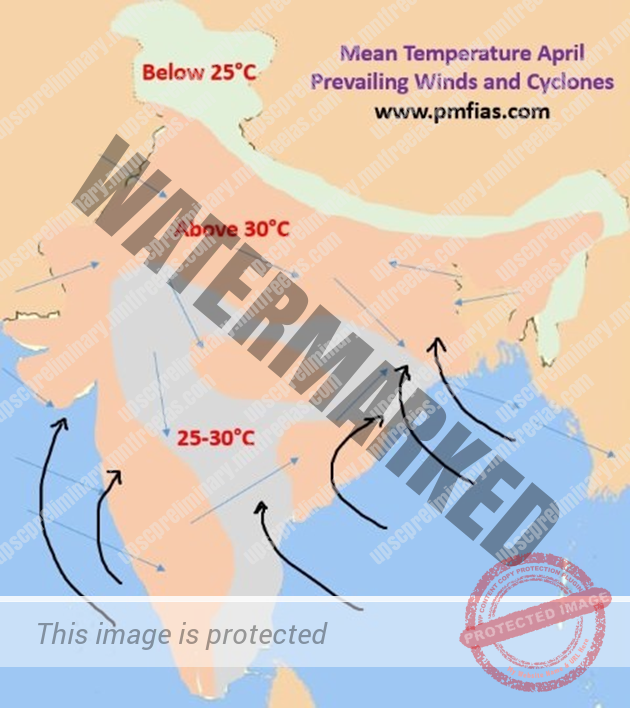
SUMMER SEASON IN INDIA
- March to June.
- High temperature and low humidity are the chief characteristics.
- Sometimes referred to as pre-monsoon period.
TEMPERATURE IN SUMMER SEASON
High sun’s insolation due to apparent movement of sun between the equator and the Tropic of Cancer.
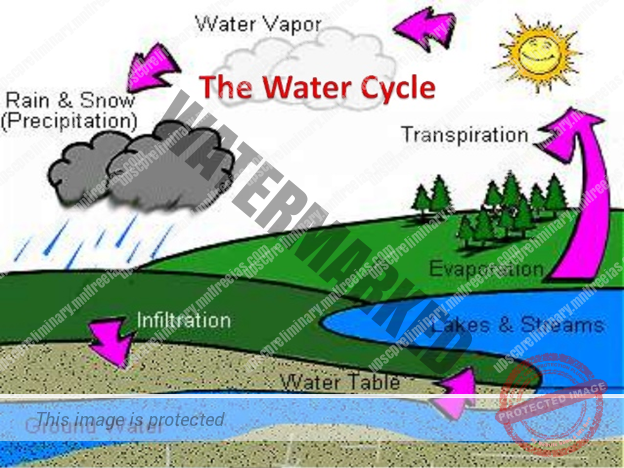
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE
Water is present in the atmosphere in three forms namely – gaseous, liquid and solid.
The moisture in the atmosphere is derived from water bodies through evaporation and from plants through transpiration. Thus, there is a continuous exchange of water between the atmosphere, the oceans and the continents through the processes of evaporation, transpiration, condensation and precipitation.
Water vapour present in the air is known as humidity
The actual amount of the water vapour present in the atmosphere is known as the absolute humidity.
It is the weight of water vapour per unit volume of air and is expressed in terms of grams per cubic meter.
The ability of the air to hold water vapour depends entirely on its temperature.
The percentage of moisture present in the atmosphere as compared to its full capacity at a given temperature is known as the Relative Humidity.
The air containing moisture to its full capacity at a given temperature is said to be saturated.
It means that the air at the given temperature is incapable of holding any additional amount of moisture at that stage. The temperature at which saturation occurs in a given sample of air is known as dew point.