- TYPES OF RAINFALL
- RAINFALL DISTRUBTION IN INDIA
UNIT 4 – CLIMATOLOGY – PART 28
TYPES OF RAINFALL
On the basis of origin, rainfall may be classified into three main types – the convectional, orographic or relief and the cyclonic or frontal.
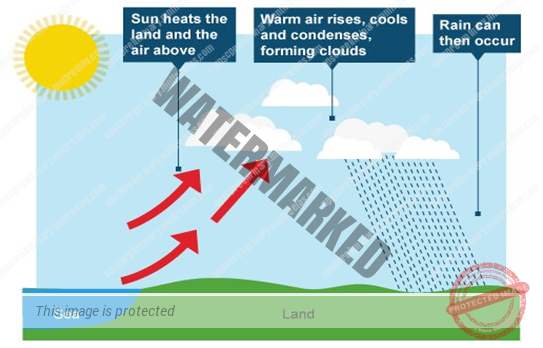
CONVENTIONAL RAIN
The air on being heated, becomes light and rises up in convection currents. As it rises, it expands and loses heat and consequently, condensation takes place and cumulous clouds are formed. With thunder and lightning, heavy rainfall takes place but this does not last.
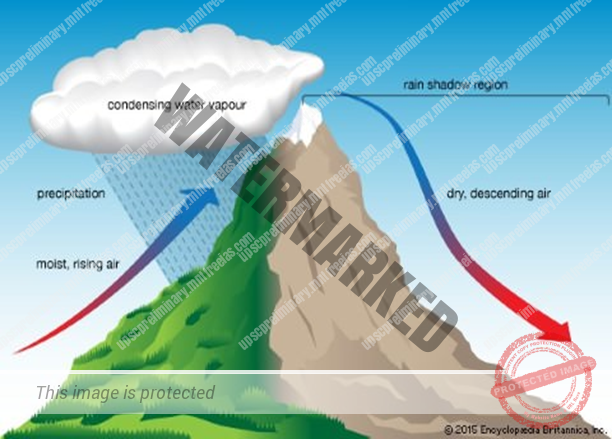
OROGRAPHIC RAIN
When the saturated air mass comes across a mountain, it is forced to ascend and as it rises, it expands; the temperature falls, and the moisture is condensed.
The chief characteristic of this sort of rain is that the windward slopes receive greater rainfall.
After giving rain on the windward side, when these winds reach the other slope, they descend, and their temperature rises.
Then their capacity to take in moisture increases and hence, these leeward slopes remain rainless and dry. The area situated on the leeward side, which gets less rainfall is known as the rain-shadow area. It is also known as the RELIEF RAIN.
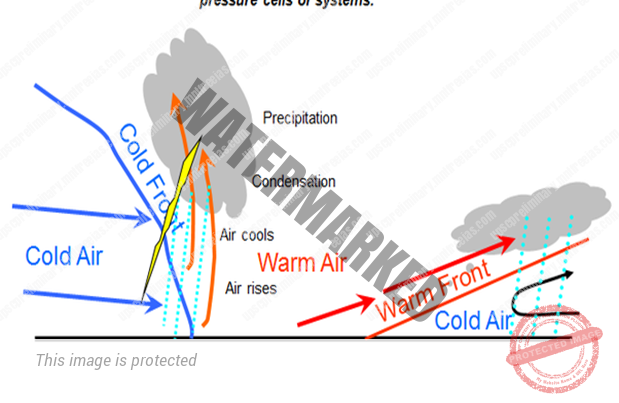
CYCLONIC RAINFALL
- Cyclonic activity causes cyclonic rain, and it occurs along the fronts of the cyclone.
- When two masses of air of unlike density, temperature, and humidity meet then it is formed.
- The layer that separates them is known AS FRONT.
- Warm front and the cold front are the two parts of the front.
- At the warm front, the warm lighter wind increases slightly over the heavier cold air.
- As the warm air rises, it cools, and the moisture present in it condenses to form clouds
- This rain falls gradually for a few hours to a few days.
RAINFALL DISTRIBUTION IN INDIA
Precipitation in India is irregular over the course of a year, with a well-defined rainy season over most of the country starting in about June and ending in September. According to the Koppen climate classification, it has seven different climatic regions:
- Tropical semi-arid
- Sub-tropical arid desert
- Sub-tropical semi-arid
- Tropical rainforest
- Tropical Savannah
- Sub-tropical humid
- Alpine
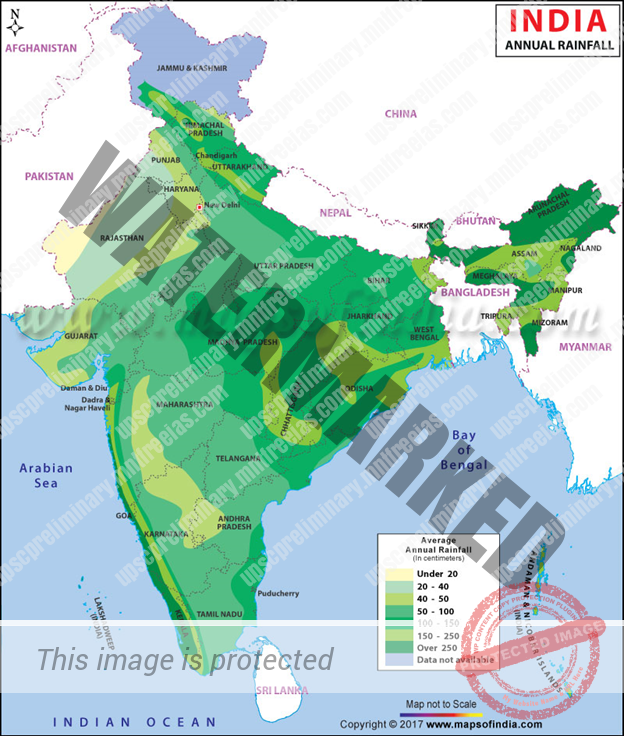
The average rainfall in India is 118 cm according to annual data from the Meteorological Department. The following is the distribution of rainfall in India:
- Extreme Precipitation regions: Northeastern regions and the windward side of the Western ghats experience an average of 400cm of annual rainfall. Areas like Assam, Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh and hilly tracts of the Western Ghats are host to tropical rainforests. The highest rainfall in India and the world is recorded at Mawsynram village of Meghalaya.
- Heavy Precipitation regions: The regions experiencing 200-300cm rainfall belong to this zone. Most of Eastern India is covered under this zone. These regions are also home to tropical rainforests. States such as West Bengal, Tripura, Nagaland, Manipur, Orissa and Bihar are included in this zone. Most of the areas in the sub-Himalayan belt also fall under this zone.
- Moderate Precipitation regions: Areas which experience 100 to 200 cm of rainfall include parts of West Bengal, Bihar, Orissa, Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, and leeward side of the Western Ghats. Wet Deciduous forests comprise the most common natural vegetation of these regions.
- Scanty Precipitation regions: Areas having 50 to 100 cm of rainfall consisting of parts of Maharashtra, Gujarat, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh. Tropical Grasslands, Savannah and Dry Deciduous forests are commonly found in these areas.
- Desert and Semi-desert Regions: These are the areas receive below 50 cm of rainfall. The states of Rajasthan, Gujarat and adjacent areas are classified as desert or semi-desert based on the amount of rainfall they receive. Some parts of Jammu & Kashmir such as the Ladakh plateau are also included in this zone as cold deserts. The vegetation consists of hardy species which can withstand extended droughts. Some areas like parts of Gujarat have Savannah vegetation in the wetter regions. The lowest rainfall in India has been recorded in Ruyli village, Rajasthan.
The rainfall distribution in India is impacted by the Thar desert and the Himalayas. Temperature and pressure changes over the Indian Ocean, the Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal and the southern part of the Pacific Ocean also play a significant role in the monsoon rains over the country.