- NATURAL VEGETATION
- LIFE IN THE DESERT
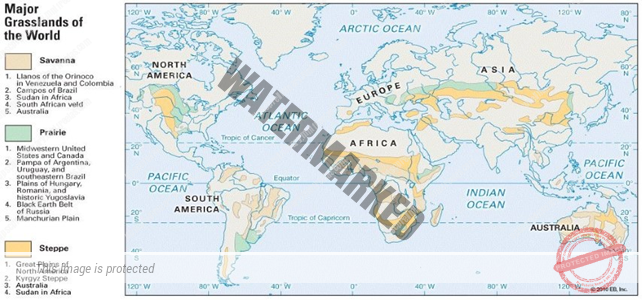
- STEEOE OR TEMPERATE GRASSLAND CLIMATE
UNIT 4 – CLIMATOLOGY – PART 35
NATURAL VEGETATION
- All deserts have some form of vegetation such as grass, scrub, herbs, weeds, roots or bulbs.
- The predominant vegetation of both hot and mid-latitude deserts is xerophytic or drought resistant scrub.
- This includes the bulbous cacti, thorny bushes, long-rooted wiry grasses and scattered dwarf acacias.
- Plants that exist in deserts have highly specialized means of adapting themselves to the arid environment.
- Most desert shrubs have long roots and are well spaced out to gather moisture, and search for ground water.
- Plants have few or no leaves and the foliage is either waxy, leathery, hairy, or needle-shaped to reduce the loss of water through transpiration.
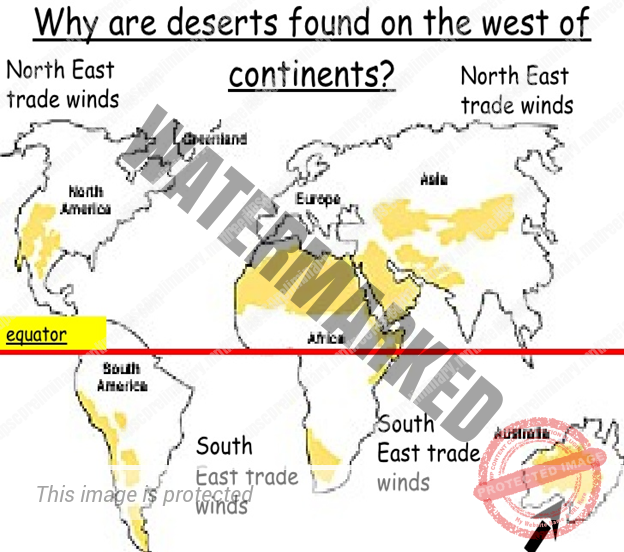
Major hot deserts in northern hemisphere are located between 20-30 degree north and on the western side of the continents. Why
The hot deserts lie along the Horse Latitudes or the Sub-Tropical High-Pressure Belts where the air is descending, a condition least favorable for precipitation of any kind to take place.
The rain-bearing Trade Winds blow off-shore and the Westerlies that are on-shore blow outside the desert limits.
Whatever winds reach the deserts blow from cooler to warmer regions, and their relative humidity is lowered, making condensation almost impossible.
There is scarcely any cloud in the continuous blue sky. The relative humidity is extremely low, decreasing from 60 per cent in coastal districts to less than 30 per cent in the desert interiors. Under such conditions, every bit of moisture is evaporated, and the deserts are thus regions of permanent drought. Precipitation is both scarce and most unreliable.
On the western coasts, the presence of cold currents gives rise to mists and fogs by chilling the on-coming air. This air is later warmed by contact with the hot land, and little rain falls. The desiccating effect of the cold Peruvian Current along the Chilean coast is so pronounced that the mean annual rainfall for the Atacama Desert is not more than 1.3 cm
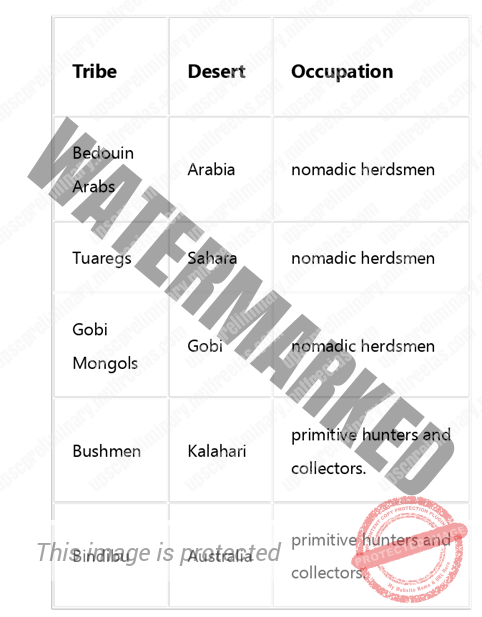
Life in the Deserts
The settled cultivators
- Modem concrete dams constructed across the Nile, e.g., Aswan and Sennar Dams improved agriculture.
- In the same way, desert cultivators rely on the Indus in Pakistan, the Tigris-Euphrates in Iraq, and the Colorado in the Imperial Valley of California.
- In the deserts, wherever there are oases (depressions where underground water reaches the surface), some form of settled life is bound to follow.
- Some of them are abnormally large like the Tafilalet Oasis in Morocco which measures 5,000 square miles.
- A wall is usually constructed around the oasis to keep out the violent dust storms called simooms.
- The most important tree is the date palm. The fruit is consumed locally and also exported.
- Other crops cultivated include maize, barley, wheat, cotton, cane sugar, fruits and vegetables.
The mining settlers
- Gold is mined in Great Australian Desert. Kalgoorlie and Coolgardie have become large towns.
- In the Kalahari Desert (thirst land), the discovery of diamonds and copper has brought many white men.
- In Atacama, in northern Chile, large mining camps have been established for the mining of caliche (cemented gravels) from which sodium nitrate, a valuable fertiliser, is extracted.
- Besides nitrates, copper is also mined. Chuquicamata is the world’s largest copper town.
- In the deserts of North America, silver is mined in Mexico, uranium in Utah and copper in Nevada.
- Discovery of oil, in many parts of the Saharan and Arabian Deserts, has transformed the region.
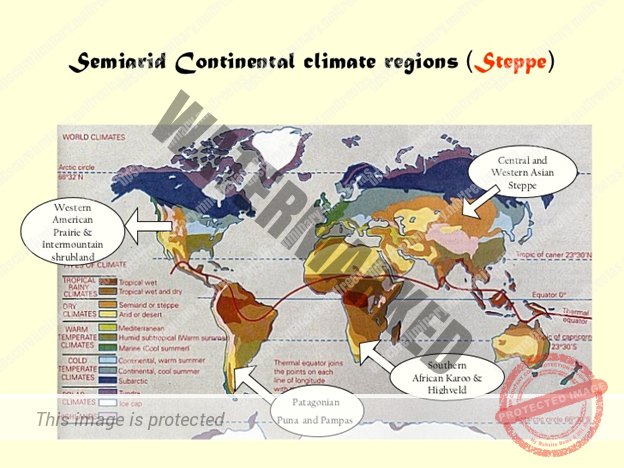
Steppe or Temperate Grassland Climate (BSK: B – Dry, S – Steppe, k – high latitude)
Steppe climate is also known as Temperate Continental Climate
Distribution
They lie in the interiors of the continents.
Lie in the Westerly wind belt [mid-latitudes or temperate region].
Grasslands are practically treeless due to continentality [deep within the interiors of the continents where rain bearing winds don’t reach].
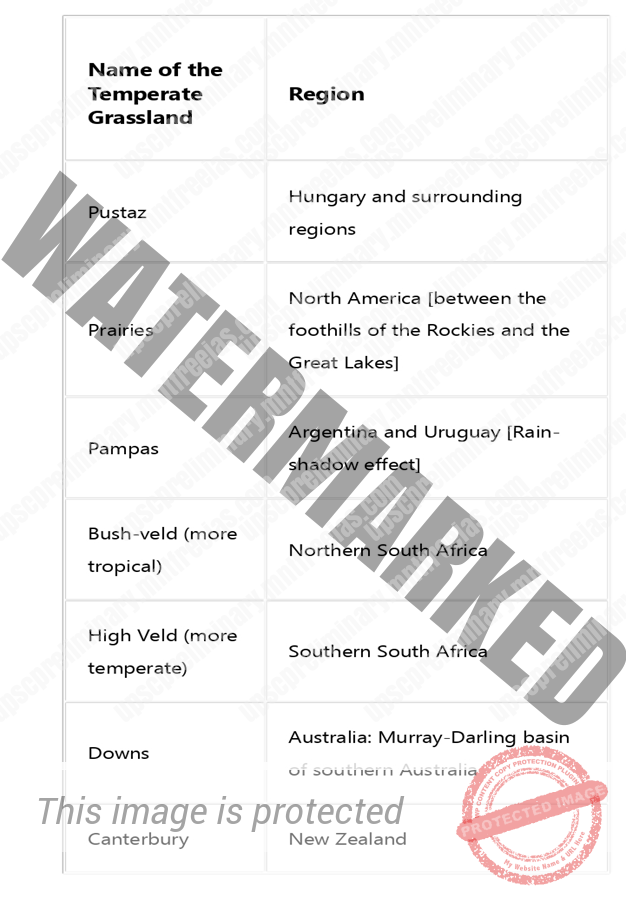
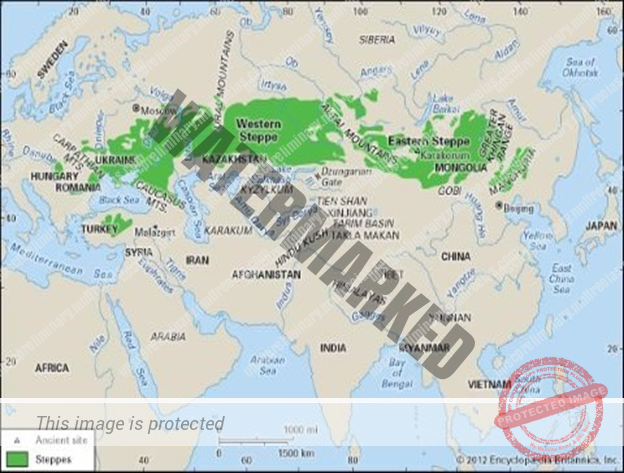
In Eurasia, they are called the Steppes, and stretch eastwards from the shores of the Black Sea to the foothills of the Altai Mountains. [2,000 miles long belt].
TEMPERATURE
Climate is continental with extremes of temperature.
Temperatures vary greatly between summer and winter.
The summers are hot, and the winters are cold.
Summers are very warm, over 18 – 20° C.
The steppe type of climate in the southern hemisphere is never severe.