- HEATING AND COOLING OF ATMOSPHERE
- TERRESTIAL RADIATION
- HEAT BUDGET OF THE PLANET EARTH
UNIT 4 – CLIMATOLOGY – PART 8
HEATING AND COOLING OF ATMOSPHERE
The atmosphere is largely transparent to short wave solar radiation
The earth after being heated by insolation transmits the heat to the atmospheric layers near to the earth in long wave form.
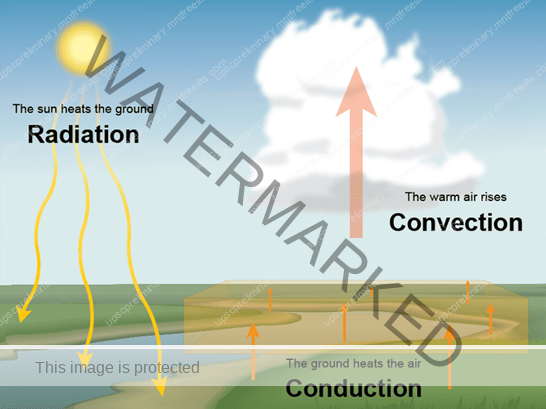
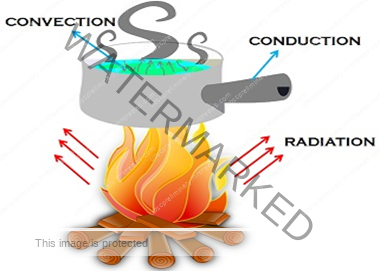
Conduction
The heat energy from the earth’s surface is transferred to the lower atmosphere also get heated which is directly in contact with the surface by the process of conduction.
Conduction takes place when two bodies of unequal temperature are in contact with one another, there is a flow of energy from the warmer to cooler body. The transfer of heat continues until both the bodies attain the same temperature, or the contact is broken. Conduction is important in heating the lower layers of the atmosphere.
Convection
The air in contact with the earth rises vertically on heating in the form of currents and further transmits the heat of the atmosphere. This process of vertical heating of the atmosphere is known as convection. The convective transfer of energy is confined only to the troposphere.
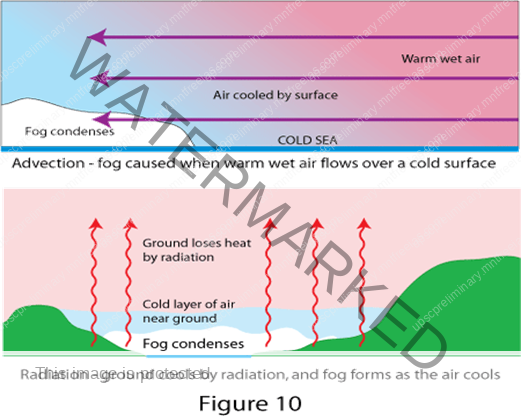
Advection
The transfer of heat through horizontal movement of air is called advection. Horizontal movement of the air is relatively more important than the vertical movement.
In middle latitudes, most of diurnal (day and night) variation in daily weather are caused by advection alone.
In tropical regions particularly in northern India during summer season local winds called ‘loo’ is the outcome of advection process.
Terrestrial Radiation:
The insolation received by the earth is in short waves forms and heats up its surface. The earth after being heated itself becomes a radiating body and it radiates energy to the atmosphere in long wave form. This energy heats up the atmosphere from below. This process is known as terrestrial radiation.
The long wave radiation is absorbed by the atmospheric gases particularly by carbon dioxide and the other greenhouse gases.
Thus, the atmosphere is indirectly heated by the earth’s radiation. The atmosphere in turn radiates and transmits heat to the space.
Finally, the amount of heat received from the sun is returned to space, thereby maintaining constant temperature at the earth’s surface and in the atmosphere.
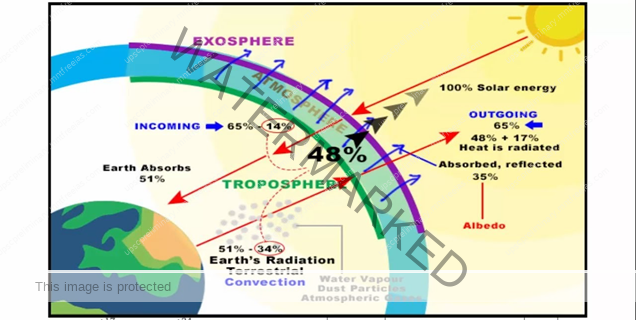
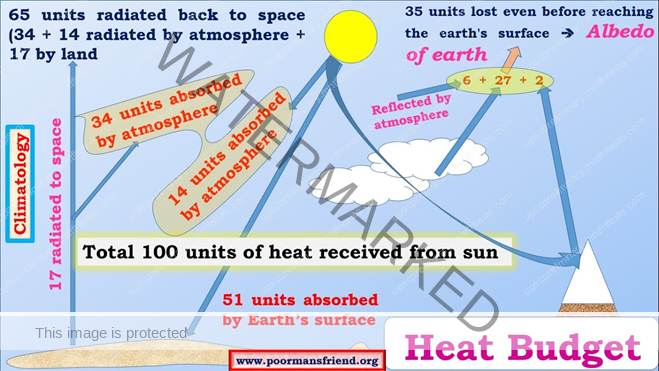
Heat Budget of the Planet Earth
The heat energy reflected, absorbed and radiated back into the space equals the energy received by the earth. Incoming radiation and the outgoing radiation pass through the atmosphere. The earth maintains its optimum temperature.
Consider that the insolation received at the top of the atmosphere is 100 per cent. While passing through the atmosphere some amount of energy is reflected, scattered and absorbed. Only the remaining part reaches the earth surface