- EVOLUTION OF EARTH
- MOTION OF THE EARTH
- EFFECTS OF EARTH’S ROTATION
- EFFECTS OF REVOLUTION OF THE EARTH
- DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ROTATION AND REVOLUTION
UNIT 2 – EARTH – PART 1
EARTH
EVOLUTION OF EARTH
The earth is almost 4.6 billion years old various geological processes and landmass which formed over these years and is responsible for the present configuration of the earth with several continents, oceans, mountain ranges, marine trenches etc.
This geological history also contains aspects like formation of atmosphere which subsequently resulted in origin of life and formation of biosphere.
MOTIONS OF THE EARTH
The earth has two basic movements:
- Rotation and 2) Revolution
- ROTATION:
Rotation means the movement of an object on its own axis. The axis is the imaginary line passing through the centre of the earth. The earth completes one rotation in 23hours, 56 minutes and 4.09 seconds. It rotates in an eastward direction opposite to the apparent movement of the sun.
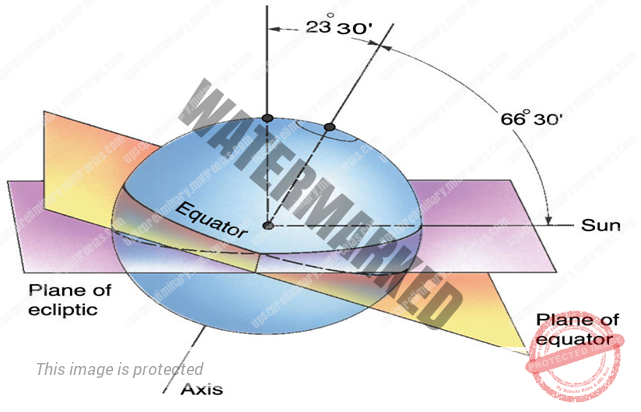
The earth’s axis is inclined at an angle of 66½° to the orbital plane as it moves around the sun,
The earth’s axis is tilted at an angle of 23½° from a perpendicular to the elliptic plane.
The velocity of earth’s rotation at the poles is nearly zero and greater at the equator.
The velocity of rotation at the equator is 1,670 km per hour.
EFFECTS OF EARTH’S ROTATION:
1) The apparent rising and setting of the sun is actually caused by the Earth’s rotation which results in the alternate occurrence of day and night.
2) The difference in time between different places on the earth is due to rotation.
3) Coriolis force formed due to rotation which results in the deflection of the winds and the ocean currents from their normal path.
4). Tide is caused by the rotation of the earth apart from the gravitational pull of the sun and the moon
5). Rotation causes a flattening of Earth at the two poles and bulging at the Equator.
REVOLUTION
The movement of the earth in its orbit around the sun in an anti-clockwise direction, (from west to east) is called revolution of the earth. The planets moving around the sun is called revolution.
Earth revolves in orbit around the sun in 365 days, 6 hours, 9 minutes with reference to the stars, at a speed ranging from 29.29 to 30.29 km/s. +The 6 hours, 9 minutes adds up to about an extra day every fourth year, which is designated A Leap Year, with the extra day added as February 29th.
The distance of the earth from sun varies from time to time due to the elliptical shape of the orbit. About January 3rd the earth is closest to the sun, and it is said to be at Perihelion. Around July 4th the earth is farthest from the sun, and it is said to be at Aphelion.
EFFECTS OF REVOLUTION OF THE EARTH
- Cycle of seasons,
- Variation in length of days and nights,
- Variation in distribution of solar energy over the earth and the temperature Zones.
SEASONS
The seasons are caused due to the combined effect of the earth’s revolution and the tilt of its axis in the same direction throughout the year. A year is usually divided into Summer, Winter, Spring and Autumn seasons.
SUMMER SOLSTICE
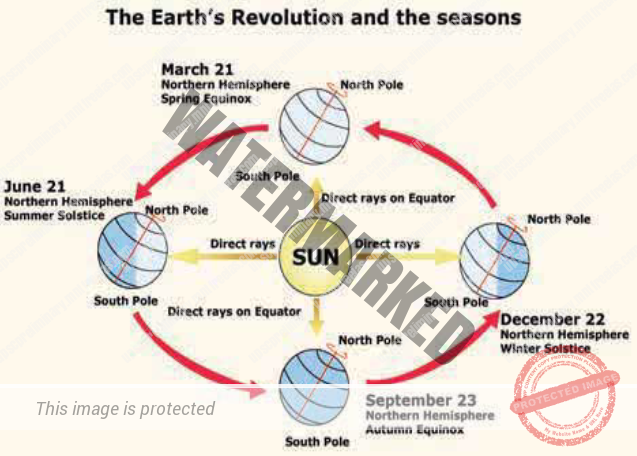
On 21st June, the Northern Hemisphere is tilted towards the sun. The rays of the sun fall directly on the Tropic of Cancer. As a result, these areas receive more heat. The areas near the poles receive less heat as the rays of the sun are slanting.
The North Pole is inclined towards the sun and the places beyond the Arctic Circle experience continuous daylight for about six months.
Since a large portion of the Northern Hemisphere is getting light from the sun, it is summer in the regions north of the equator. The longest day and the shortest night at these places occur on 21st June. It is winter season there. The nights are longer than the days. This position of the earth is called the Summer Solstice.
WINTER SOLSTICE
On 22nd December, the Tropic of Capricorn receives direct rays of the sun as the South Pole tilts towards it. As the sun’s rays fall vertically at the Tropic of Capricorn (23½° S), a larger portion of the Southern Hemisphere gets light. Therefore, it is summer in the Southern Hemisphere with longer days and shorter nights. The reverse happens in the Northern Hemisphere. This position of the earth is called the Winter Solstice.
EQUINOX
On 21st March and September 23rd, direct rays of the sun fall on the equator. At this position, neither of the poles is tilted towards the sun; so, the whole earth experiences equal days and equal nights. This is called an equinox.
On 23rd September, it is autumn season in the Northern Hemisphere and spring season in the Southern Hemisphere. The opposite is the case on 21st March
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ROTATION AND REVOLUTION
Rotation Spinning of the earth from west to east on its axis. It takes 24 hours to complete a rotation (or a day). Rotation causes days and nights to alternate, tides, deflection of winds and ocean currents and also gives the earth its shape. | Revolution Movement of the earth around the sun in its elliptical orbit. It takes 365¼ days to complete one revolution (or a year). Revolution results in the varying lengths of day and night, changes in the altitude of the midday sun and change of seasons |