- TRANSPORT AND COMMUNICATION
UNIT 9 – ECONOMIC GEOGRAPHY – PART 6
TRANSPORT AND COMMUNICATION:
Transport plays important part in economic growth and globalization. It supports greater reach and availability for the products in marketplace. Thus, transport infrastructure in prerequisite for the development of a country.
Means of Transport
Roadways:
India has the second largest road network in the world with total length of around 5.4 million km.
It plays a significant role in carrying goods and people in all parts of the country. Particularly, the rural economy depends upon the road transport. For short distance journey, roads are more suitable.
They supplement the railways by linking the interior areas with railway heads. Roads are ideal for the promotion of tourism in the country.
Importance of Roadways:
- Roads play a very important role in the transportation of goods and passengers for short and medium distances.
- It is comparatively easy and cheap to construct and maintain roads.
- Its cost of construction and maintenance is far less than that of the railway
Classification of Roads:
Nagpur plan 1943 classified roads as National Highways, State highways, District Roads and Rural Roads.
- National Highways:
These are primary roads connecting state capitals, big cities, important ports and meant for inter-state and strategic defence movements.
The length of national Highway is around 96,400 km. Though it consists only 3% of total roadways, it handles 40% of the total road traffic.
National Highways are constructed and maintained by the Central Government. An autonomous body called NHAI (National Highways Authority of India) was formed in 1995 and entrusted with the responsibility of development, maintenance, and operation of National Highways. NHAI implements the NHDP (National Highway Development Project) one of largest programmes of road development overtaken in any country with shortest time span for completion.
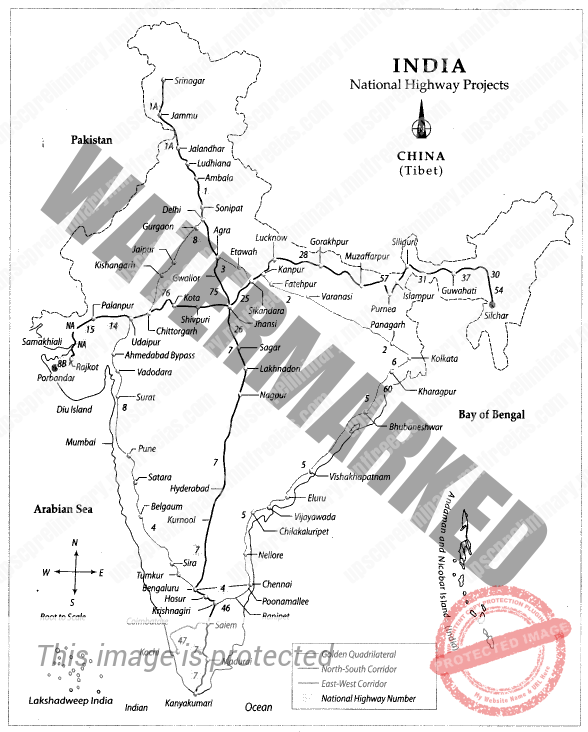
Golden Quadrilateral:
Comprising National Highway connecting Delhi-Mumbai-Chennai-Kolkata by son lane superhighways. With total length of 5,486km. Chennai Kolkata is the longest side in these four sides with 1,684 km.
State Highways:
This road connects state capitals with district headquarters and other important towns. These are constructed and maintained by state government. State Highways constitute 5.46% of total road length that constitutes for nearly 114000 km in India.
Although construction and maintenance of state highways is the responsibility of state governments the centre provides about Rs. 1000 Crore under Central Road Found (CRF).
- District Roadways:
These roads connect different parts of the districts with district headquarters, Industrial centres, and markets. Development and maintenance of these roads falls under the purview of Zila Parishads.
- Rural Roads:
These roads connect villages with neighbouring towns. 80% of the total Indian roads are classified as rural roads.
PMGSY:
on 2005 Central Government rolled of a centrally sponsored scheme known as PRADAN MAINDRI GRAM SADAK YOJANA to provide good all weathery road connection to unconnected villages.
Other Roads:
This category includes Border Roads and International Highways.
Border Roads Organisation (1960) was established in the view of connecting strategically important roads along the northern and northeastern boundary of the country. it constructed the world’s highest motorable road joining Chandigarh with Manali.
BRO has been functioning under the administrative control of Ministry of Defense.
BHARAT MALA: Bharatmala Pariyajana is a new umbrella program for the highways sector that focuses on optimizing efficiency of freight and passenger movement across the country by bridging critical infrastructure gaps through effective interventions like development of Economic Corridors, Inter Corridors and Feeder Routes, National Corridor Efficiency Improvement, Border and International connectivity roads, Coastal and Port connectivity roads and Green-field expressways.
BHARATMALA PROJECT CATEGORY
Economic Corridor – As per the guidelines of the road construction project, the construction of 9000kms of Economic Corridors will be undertaken by the central government.
Feeder Route or Inter Corridor – The total length of the roads, which fall under the Feeder Route or Inter Corridor category, is a whopping 6000kms.
National Corridor Efficiency Improvement – 5000kms of roads, constructed under the scheme will fall in the category of National Corridor for the better connection between roads.
Border Road and International Connectivity – Connecting the cities and remote areas, which are situated in the border regions, the project has kept provision for constructing 2000kms roads that fall in the Border Road or International Connectivity category.
Port Connectivity and Coastal Road – To connect the areas that are dotted along the shorelines and important ports, the central government has ordered the construction of 2000km of roads.
Green Field Expressway – The main stress will be given on the construction and development of Green Field Expressway for better management of traffic and freight.
Balance NHDP Works – Under the last segment, the project will see a construction and maintenance of about 10,000kms of new roads.
List of Important National Highways of India
National Highways | Connectivity |
NH -1 | Delhi to Amritsar (via Ambala and Jalandhar) |
NH-1 A | Jalandhar to Uri (via Madhavpur, Jammu, Srinagar, and Baramulla) |
NH-2 | Delhi to Kolkata (via Mathura and Varanasi) |
NH-3 | Agra to Mumbai (via Gwalior, Indore and Nasik) |
NH-4 | Thane (Mumbai) to Chennai (via Pune, Belgaum, Hubli, Bangalore and Ranipet) |
NH- 5 | Bahragoda (Near Kolkata) to Chennai (via Cuttack, Visakhapatnam and Vijayawada) |
NH-6 | Hazira to Kolkata (via Nagpur, Raipur, and Sambalpur, Dhule) |
NH-7 | Varanasi to Kanyakumari (via Nagpur, Bangalore and Madhuri) |
NH-8 | Delhi to Mumbai (Jaipur, Ahmadabad, and Vadodara) |
NH-9 | Pune to Machilipatnam (via Sholapur and Hyderabad, Vijayawada) |
NH-10 | Delhi to Fazilka proceeding to Indo-Pak border |
NH-14 | Beawar to Radhanpur (Sirohi) |
NH-15 | Pathankot to Kandla (Near Thar Desert) |
NH-24 | Delhi to Lucknow |
NH-39 | Numaligarh to Indo-Myanmar Border |