|
UNIT 2 – BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLE – PART 5
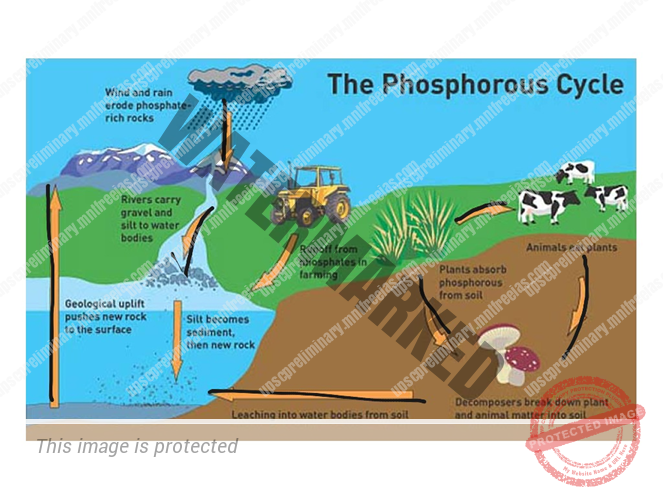
Phosphorous cycle
The transport and chemical transformation of phosphorus through the lithosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere are called phosphorus cycle.
The atmosphere does not play a significant role in the movement of phosphorus because phosphorus or phosphorus-based compounds are solids available in normal ranges of temperature and pressure of the earth. Most of the phosphorus remains within rocks, sediments, sand and the ocean floor with a fraction in living biomass. Phosphorus moves along trophic levels in an ecosystem by plant growth, herbivores and carnivores.
Note- Phosphates are effective fertilizers but they also cause pollution in lakes and streams. Over enrichment of it can lead to algae blooms. This excess of algae causes increased consumption by bacteria which lead to higher bacterial concentration. In this process, bacteria use much of dissolved oxygen in the water for cellular respiration and cause the death of fish due to oxygen deprivation.
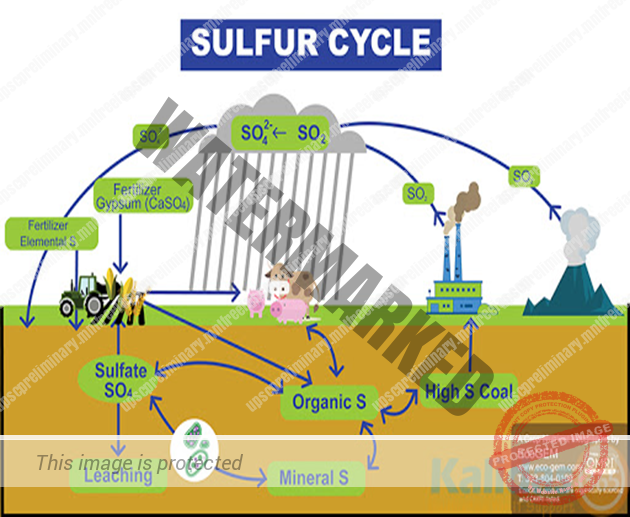
Sulphur cycle
Sulphur Cycle is a type of sedimentary cycle which is sediments based. It does not involve circulation (in the form of gases) through the atmosphere as in case of gaseous cycles. It consists of all such processes through which Sulphur is transferred from rocks to the living systems and vice versa.
Sulphur is used in the process of proteins and vitamins production. Proteins consist of amino acids that contain Sulphur atoms like thiophene. When Sulphur is dissolved in water, plants absorb them. Animals consume these plants so that they take up enough Sulphur to maintain their health.
- Most of the earth’s Sulphur tied up in the rocks and salts or buried deep in the ocean in oceanic sediments.
- Sulphur can also be found in the atmosphere. It enters the atmosphere by both natural and human sources.
- Natural sources can be volcanic eruptions, bacterial processes and evaporation from water or decaying organisms.
- Human activities mainly from industrial purposes where Sulphur dioxide and hydrogen Sulphide gases are emitted on a wide scale.
- When Sulphur dioxide enters the atmosphere, it reacts with oxygen to produce Sulphur trioxide or with other chemicals to make Sulphur salts. Sulphur dioxide also reacts with water to produce Sulphuric acid. All these particles react with rain and fall back onto Earth as acid deposition.
- The particles then are absorbed by plants again and are released back into the atmosphere and then Sulphur cycle will start over again.
The entire Earth biosphere is a closed system so that nutrients are neither imported nor exported from the biosphere. The biogeochemical cycle also referred to as the cycle of nature because they link together all organisms and abiotic component.