- ELEMENTS
- METAL, NON-METAL & COMPOUND
- ATOMS & MOLECULES
UNIT 6 – DISTILLATION – PART 2
ELEMENTS
- In 1661, Robert Boyle was the first scientist who used the term element; Antoine Laurent Lavoisier, a French chemist, was the first who experimentally define the term element.
Definition:
‘… Element is as a basic form of matter that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by a chemical reaction….”
- Elements normally can be categorized as
1.Metals,
- Non-Metals.
- Metalloids.
Elements can only be broken into subatomic particles or transmuted into other elements by nuclear reactions. At present, there are 118 known elements.
If atoms of an element carry an electrical charge, they are called ions. Atoms of an element with different numbers of Neutrons Are Called Isotopes. Sometimes isotopes also have their own names, but they are still examples of an element.
The term isotopes was coined by Scottish doctor Margaret Todd in 1913. She suggested it to chemist Frederick Soddy. The word comes from the Greek words isos (equal) and topos (place). Isotopes of an element occupy the same position on the periodic table.
For example: Protium, Deuterium, And Tritium are all isotopes of the element hydrogen. Elements can take different forms called allotropes, but this doesn’t change their chemical identity.
For example: Diamond and Graphite are both pure elemental Carbon.
METAL
- A solid material, which typically is hard, ductile, malleable, shiny, and fusible with good electrical and thermal conductivity, is known as metal. E.g., Gold, Silver, Copper, Aluminum,
- Approximately three-quarters of all known chemical elements are metals. The most abundant varieties in the Earth’s crust are aluminum, iron, calcium, sodium, potassium, and magnesium.
The vast majority of metals are found in ores (mineral-bearing substances), but a few such as copper, gold, platinum, and silver frequently occur in the free state because they do not readily react with other elements.
- Metals differ widely in their chemical reactivity.
The Most Reactive include Lithium, Potassium, and Radium, whereas those of Low Reactivity are Gold, Silver, Palladium, And Platinum.
- Mercury is the only metal that remains liquid at room temperature.
NON-METAL
- All elements or substances, which are not metals, are known as non-metals. E.g., Hydrogen, Oxygen, Iodine, Carbon, etc.
- Non-metals have variety of colors, and they are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
- Non-metals are not lustrous, sonorous, or malleable.
COMPOUND
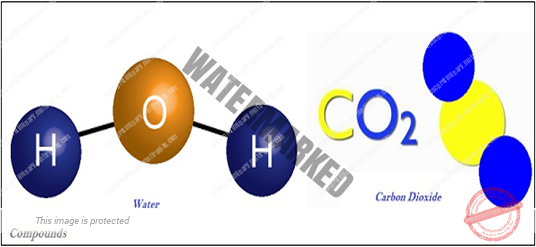
- A substance, composed of two or more elements, is known as ‘compound.’
- Compound is the result of the chemically combination of two or more elements in a fixed proportion.
- Properties of a compound are somehow different from its constituent elements, whereas the properties of a mixture are the same as of its constituting elements or compounds.
ATOMS & MOLECULES
INTRODUCTION
Around 500 BC, an Indian Philosopher Maharishi Kanad, first time postulated the concept of indivisible part of matter and named it ‘parmanu.’
- In 1808, John Daltonused the term ‘atom’ and postulated the atomic theory to the study of matter.
DALTON’S ATOMIC THEORY
- According to Dalton’s atomic theory, all matter, whether an element, a compound or a mixture is composed of small particles called atoms.
- According to Dalton’s atomic theory, all matters, whether they are elements, compounds, or mixtures, are composed of small particles known as atoms.
SALIENT FEATURES OF DALTON’S ATOMIC THEORY
- All matter is made of very miniscule particles known as atoms.
- Atom is an indivisible particle, which cannot be created or destroyed through chemical reaction.
- All atoms of an element are identical in mass and chemical properties whereas, atoms of different elements have different masses and chemical properties.
- To form a compound, atoms are combined in the ratio of small whole numbers.
- In a given compound, the relative number and kinds of atoms are constant.
ATOMIC MASS
- The mass of an atom of a chemical element; it is expressed in Atomic Mass Units (Symbol Is U).
- The atomic mass is roughly equivalent to the number of protons and neutrons present in the atom.
- “…. One atomic mass unit is a mass unit equal to the exactly one-twelfth (1/12th) the mass of one atom of carbon-12 and the relative atomic masses of all elements have been calculated with respect to an atom of carbon-12….”
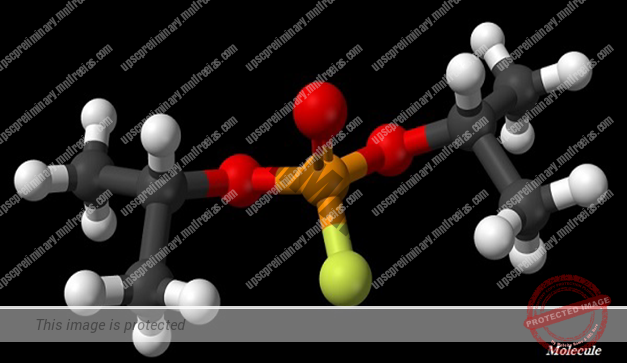
MOLECULE
- The smallest particle of an element or a compound, which is capable to exist independently and shows all the properties of the respective substance.
- A molecule, normally, is a group of two or more atoms which are chemically bonded together.
- Atoms of the same element or of different elements can join (with chemical bond) together to form molecules.
- The number of atoms that constitute a molecule is known as its atomicity.
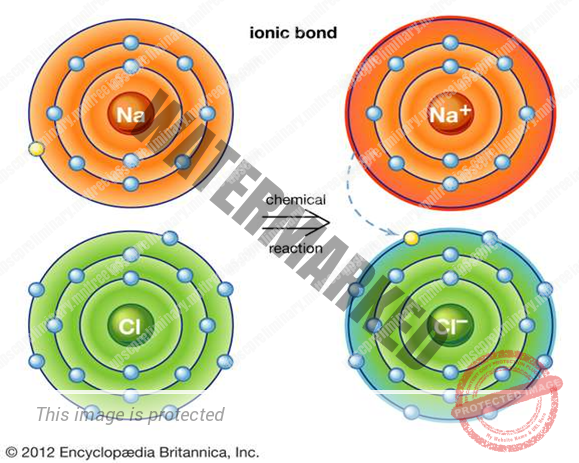
ION
- A charged particle is known as ion. Ionic bond, also called electrovalent bond, type of linkage formed from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ionsin a chemical compound. Such a bond forms when the valence (outermost) electrons of one atom are transferred permanently to another atom. The atom that loses the electrons becomes a positively charged Ion (Cation), while the one that gains them becomes a Negatively Charged Ion (Anion). A brief treatment of ionic bonds follows.