- WAVES
UNIT 9 – PHYSICS - PROPERTIES OF MATTER – PART 4
WAVES:
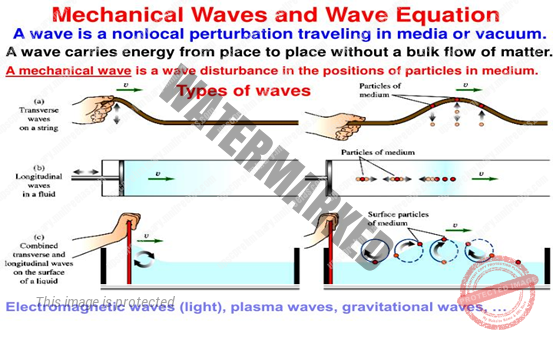
- Mechanical waves require a material medium to travel (air, water, ropes).
- THESE WAVES ARE DIVIDED INTO THREE DIFFERENT TYPES.
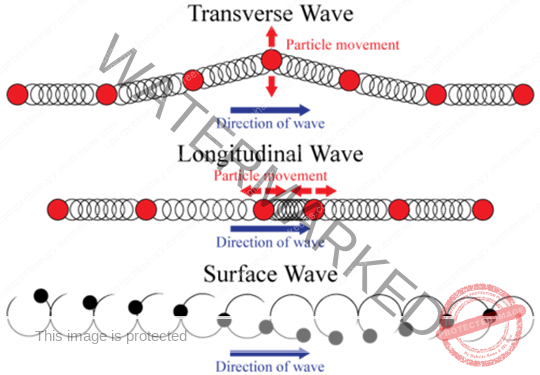
- Transverse waves cause the medium to move perpendicular to the direction of the wave.
- Longitudinal waves cause the medium to move parallel to the direction of the wave.
- Surface waves are both transverse waves and longitudinal waves mixed in one medium.
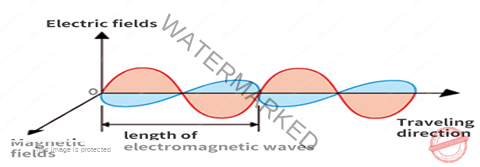
Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium to travel (light, radio).
- Matter waves are produced by electrons and particles.
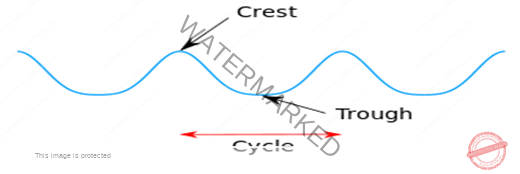
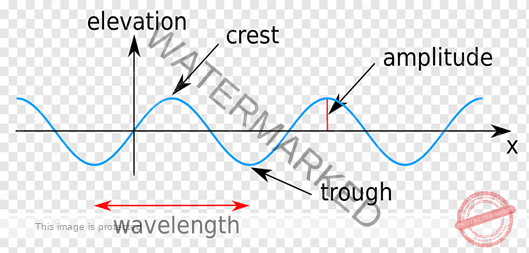
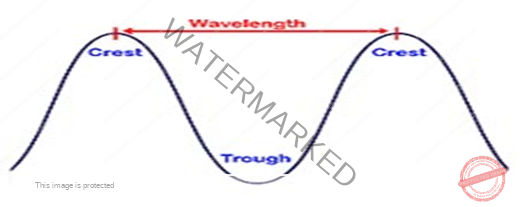
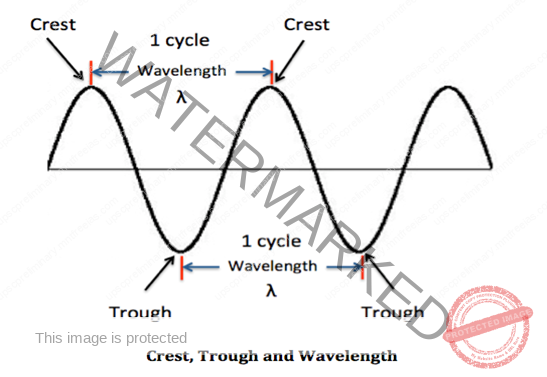
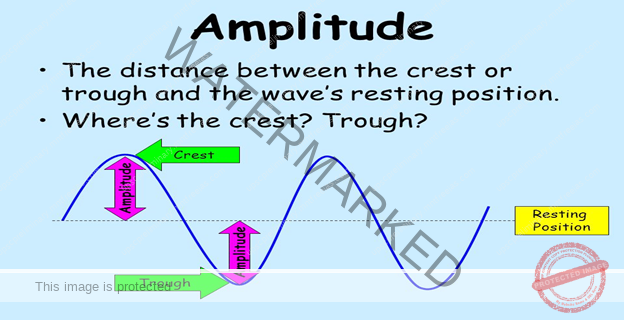
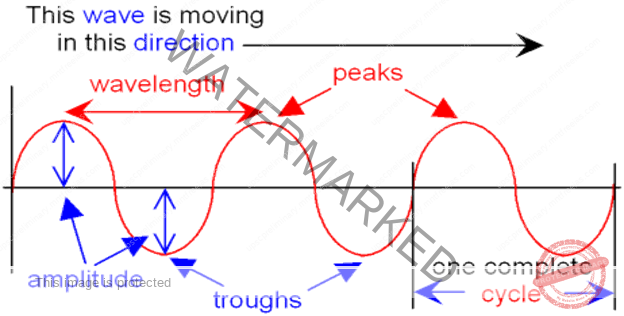
- A point of maximum positive displacement in a wave, is called crest, and a point of maximum negative displacement is called TROUGH.
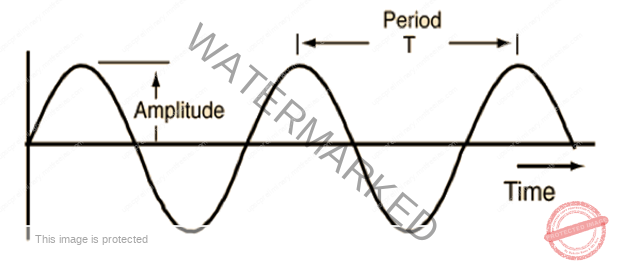
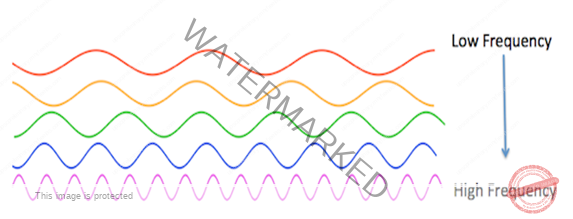
- Measuring Waves: Any point on a transverse wave moves up and down in a repeating pattern. The shortest time that a point takes to return to the initial position (one vibration) is called period, T.
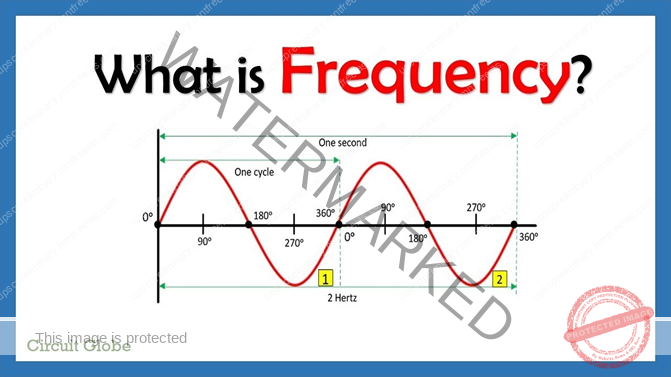
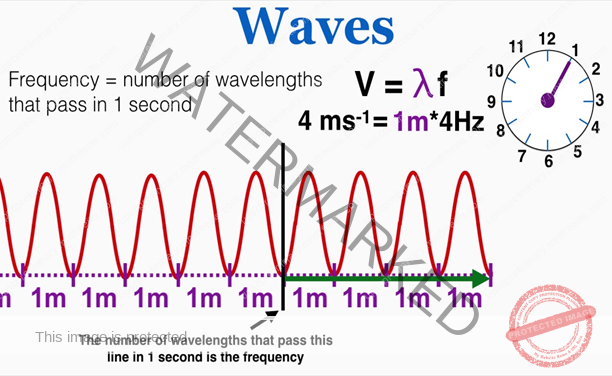
- The number of vibrations per second is called frequency and is measured in hertz (Hz). Herat’s the equation for frequency: f = 1 / T
- The shortest distance between peaks, the highest points, and troughs, the lowest points, is the wavelength,
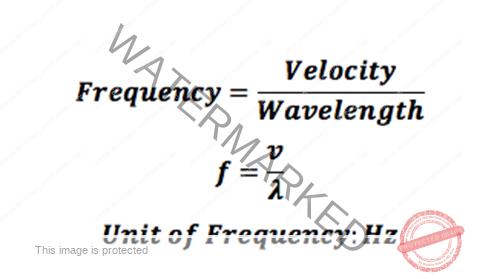
- By knowing the frequency of a wave and its wavelength, we can find its speed. Here is the equation for the velocity of a wave:
However, the velocity of a wave is only affected by the properties of the medium. It is not possible to increase the speed of a wave by increasing its wavelength. By doing this, the number of vibrations per second decreases and therefore the velocity remains the same.
- The amplitude of a wave is the distance from a crest to where the wave is at equilibrium. The amplitude is used to measure the energy transferred by the wave. The bigger the distance, the greater the energy transferred.


[pvc_stats postid="" increase="1" show_views_today="1"]
